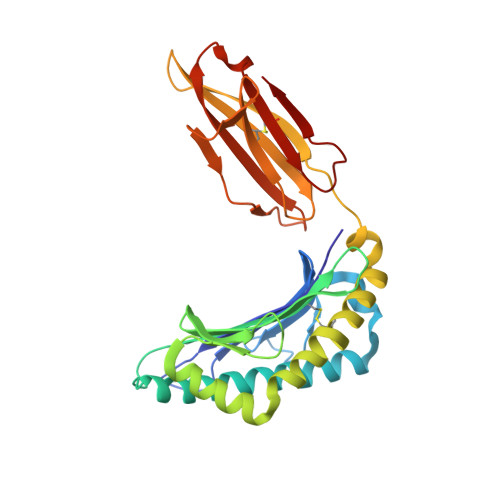
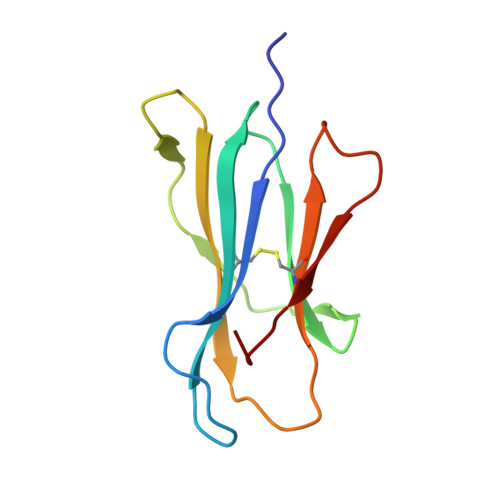
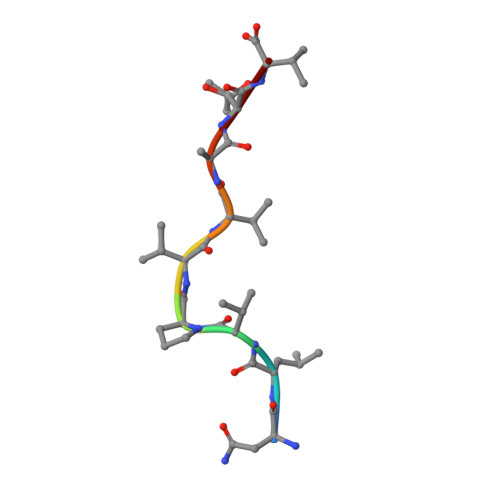
Structural bases for the affinity-driven selection of a public TCR against a dominant human cytomegalovirus epitope.
Gras, S., Saulquin, X., Reiser, J.B., Debeaupuis, E., Echasserieau, K., Kissenpfennig, A., Legoux, F., Chouquet, A., Le Gorrec, M., Machillot, P., Neveu, B., Thielens, N., Malissen, B., Bonneville, M., Housset, D.(2009) J Immunol 183: 430-437
- PubMed: 19542454
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0900556
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GSN, 3GSO, 3GSQ, 3GSR, 3GSU, 3GSV, 3GSW, 3GSX - PubMed Abstract:
Protective T cell responses elicited along chronic human CMV (HCMV) infections are sometimes dominated by CD8 T cell clones bearing highly related or identical public TCR in unrelated individuals. To understand the principles that guide emergence of these public T cell responses, we have performed structural, biophysical, and functional analyses of an immunodominant public TCR (RA14) directed against a major HLA-A*0201-restricted HCMV Ag (pp65(495-503)) and selected in vivo from a diverse repertoire after chronic stimulations. Unlike the two immunodominant public TCRs crystallized so far, which focused on one peptide hotspot, the HCMV-specific RA14 TCR interacts with the full array of available peptide residues. The conservation of some peptide-MHC complex-contacting amino acids by lower-affinity TCRs suggests a shared TCR-peptide-MHC complex docking mode and supports an Ag-driven selection of optimal TCRs. Therefore, the emergence of a public TCR of an oligoclonal Ag-specific response after repeated viral stimulations is based on a receptor displaying a high structural complementarity with the entire peptide and focusing on three peptide hotspots. This highlights key parameters underlying the selection of a protective T cell response against HCMV infection, which remains a major health issue in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation.
- Institut de Biologie Structurale Jean-Pierre Ebel, CEA, CNRS, UJF, PSB, Grenoble, France.
Organizational Affiliation: