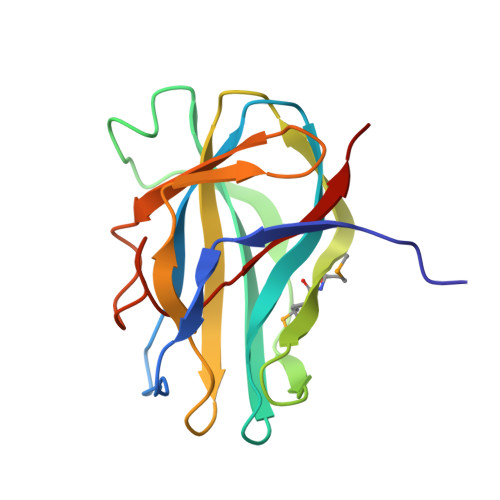
Structures of PHR domains from Mus musculus Phr1 (Mycbp2) explain the loss-of-function mutation (Gly1092-->Glu) of the C. elegans ortholog RPM-1.
Sampathkumar, P., Ozyurt, S.A., Miller, S.A., Bain, K.T., Rutter, M.E., Gheyi, T., Abrams, B., Wang, Y., Atwell, S., Luz, J.G., Thompson, D.A., Wasserman, S.R., Emtage, J.S., Park, E.C., Rongo, C., Jin, Y., Klemke, R.L., Sauder, J.M., Burley, S.K.(2010) J Mol Biology 397: 883-892
- PubMed: 20156452
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GBW, 3HWJ - PubMed Abstract:
PHR [PAM (protein associated with Myc)-HIW (Highwire)-RPM-1 (regulator of presynaptic morphology 1)] proteins are conserved, large multi-domain E3 ubiquitin ligases with modular architecture. PHR proteins presynaptically control synaptic growth and axon guidance and postsynaptically regulate endocytosis of glutamate receptors. Dysfunction of neuronal ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation is implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases. PHR proteins are characterized by the presence of two PHR domains near the N-terminus, which are essential for proper localization and function. Structures of both the first and second PHR domains of Mus musculus (mouse) Phr1 (MYC binding protein 2, Mycbp2) have been determined, revealing a novel beta sandwich fold composed of 11 antiparallel beta-strands. Conserved loops decorate the apical side of the first PHR domain (MmPHR1), yielding a distinct conserved surface feature. The surface of the second PHR domain (MmPHR2), in contrast, lacks significant conservation. Importantly, the structure of MmPHR1 provides insights into a loss-of-function mutation, Gly1092-->Glu, observed in the Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog RPM-1.
- Eli Lilly and Company, Lilly Biotechnology Center, 10300 Campus Point Drive, Suite 200, San Diego, CA 92121, USA. sampathkumarpa@lilly.com
Organizational Affiliation: