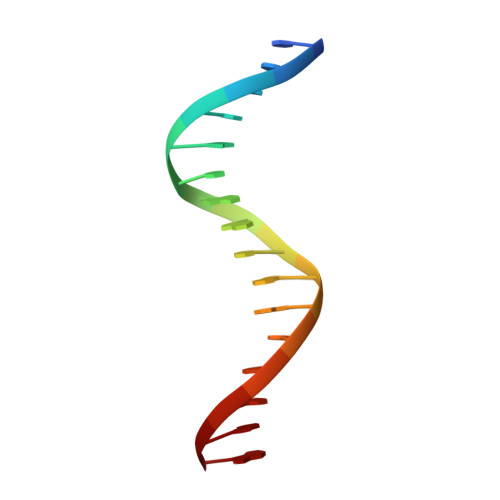
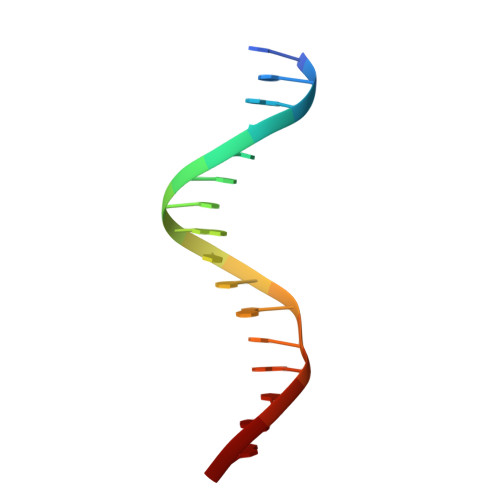
Crystal structure of the arginine repressor protein in complex with the DNA operator from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Cherney, L.T., Cherney, M.M., Garen, C.R., Lu, G.J., James, M.N.(2008) J Mol Biology 384: 1330-1340
- PubMed: 18952097
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ERE - PubMed Abstract:
The arginine repressor (ArgR) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is a gene product encoded by the open reading frame Rv1657. It regulates the L-arginine concentration in cells by interacting with ARG boxes in the promoter regions of the arginine biosynthesis and catabolism operons. Here we present a 2.5-A structure of MtbArgR in complex with a 16-bp DNA operator in the absence of arginine. A biological trimer of the protein-DNA complex is formed via the crystallographic 3-fold symmetry axis. The N-terminal domain of MtbArgR has a winged helix-turn-helix motif that binds to the major groove of the DNA. This structure shows that, in the absence of arginine, the ArgR trimer can bind three ARG box half-sites. It also reveals the structure of the whole MtbArgR molecule itself containing both N-terminal and C-terminal domains.
- Group in Protein Structure and Function, Department of Biochemistry, University of Alberta, 431 Medical Sciences Building, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2H7.
Organizational Affiliation: