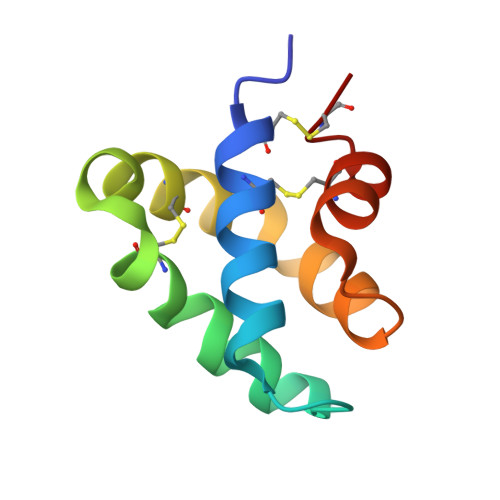
Structures of the human ceramide activator protein saposin D.
Popovic, K., Prive, G.G.(2008) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 64: 589-594
- PubMed: 18453694
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444908003120
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BQP, 3BQQ - PubMed Abstract:
Saposin D is a sphingolipid activator protein required for the lysosomal breakdown of ceramide to a fatty acid and sphingosine by acid ceramidase. The crystal structure of saposin D has been determined in two different crystal forms, resulting in a total of six crystallographically independent views of this small 80-amino-acid protein. All of the structures are highly similar and reveal the monomeric form of the saposin fold previously seen in the crystal structures of saposins A and C. Saposin D is slightly more compact than the related saposins A and C owing to a slight repositioning of the 'stem' and 'hairpin' regions of the protein.
- Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: