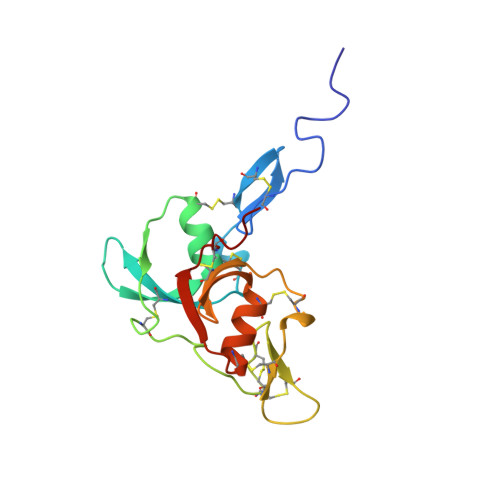
Solution Structure of Factor I-Like Modules from Complement C7 Reveals a Pair of Follistatin Domains in Compact Pseudosymmetric Arrangement.
Phelan, M.M., Thai, C.T., Soares, D.C., Ogata, R.T., Barlow, P.N., Bramham, J.(2009) J Biological Chem 284: 19637
- PubMed: 19419965
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M901993200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WCY - PubMed Abstract:
Factor I-like modules (FIMs) of complement proteins C6, C7, and factor I participate in protein-protein interactions critical to the progress of a complement-mediated immune response to infections and other trauma. For instance, the carboxyl-terminal FIM pair of C7 (C7-FIMs) binds to the C345C domain of C5 and its activated product, C5b, during self-assembly of the cytolytic membrane-attack complex. FIMs share sequence similarity with follistatin domains (FDs) of known three-dimensional structure, suggesting that FIM structures could be reliably modeled. However, conflicting disulfide maps, inconsistent orientations of subdomains within FDs, and the presence of binding partners in all FD structures led us to determine the three-dimensional structure of C7-FIMs by NMR spectroscopy. The solution structure reveals that each FIM within C7 contains a small amino-terminal FOLN subdomain connected to a larger carboxyl-terminal KAZAL domain. The open arrangement of the subdomains within FIMs resembles that of first FDs within structures of tandem FDs but differs from the more compact subdomain arrangement of second or third FDs. Unexpectedly, the two C7-FIMs pack closely together with an approximate 2-fold rotational symmetry that is rarely seen in module pairs and has not been observed in FD-containing proteins. Interfaces between subdomains and between modules include numerous hydrophobic and electrostatic contributions, suggesting that this is a physiologically relevant conformation that persists in the context of the parent protein. Similar interfaces were predicted in a homology-based model of the C6-FIM pair. The C7-FIM structures also facilitated construction of a model of the single FIM of factor I.
- Edinburgh Biomolecular NMR Unit, University of Edinburgh, West Mains Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JJ, Scotland, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: