Crystal Structure of the Human Foxo3A-Dbd/DNA Complex Suggests the Effects of Post-Translational Modification.
Tsai, K.-L., Sun, Y.-J., Huang, C.-Y., Yang, J.-Y., Hung, M.-C., Hsiao, C.-D.(2007) Nucleic Acids Res 35: 6984
- PubMed: 17940099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm703
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2UZK - PubMed Abstract:
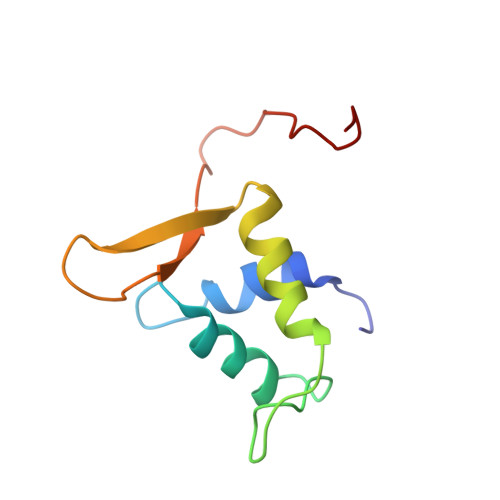
FOXO3a is a transcription factor of the FOXO family. The FOXO proteins participate in multiple signaling pathways, and their transcriptional activity is regulated by several post-translational mechanisms, including phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination. Because these post-translational modification sites are located within the C-terminal basic region of the FOXO DNA-binding domain (FOXO-DBD), it is possible that these post-translational modifications could alter the DNA-binding characteristics. To understand how FOXO mediate transcriptional activity, we report here the 2.7 A crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of FOXO3a (FOXO3a-DBD) bound to a 13-bp DNA duplex containing a FOXO consensus binding sequence (GTAAACA). Based on a unique structural feature in the C-terminal region and results from biochemical and mutational studies, our studies may explain how FOXO-DBD C-terminal phosphorylation by protein kinase B (PKB) or acetylation by cAMP-response element binding protein (CBP) can attenuate the DNA-binding activity and thereby reduce transcriptional activity of FOXO proteins. In addition, we demonstrate that the methyl groups of specific thymine bases within the consensus sequence are important for FOXO3a-DBD recognition of the consensus binding site.
- Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan.
Organizational Affiliation: