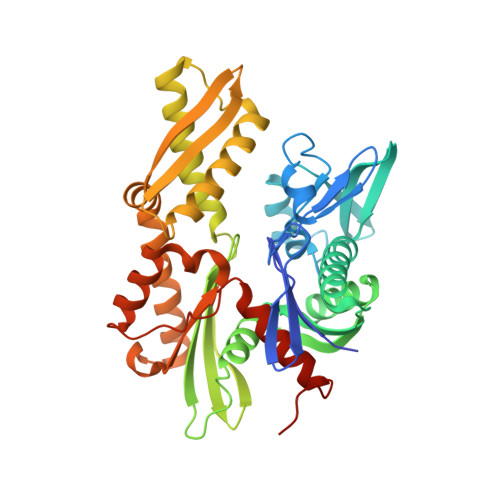
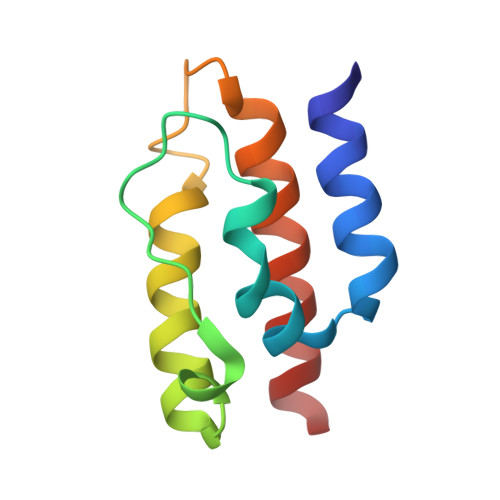
Structural basis of J cochaperone binding and regulation of Hsp70.
Jiang, J., Maes, E.G., Taylor, A.B., Wang, L., Hinck, A.P., Lafer, E.M., Sousa, R.(2007) Mol Cell 28: 422-433
- PubMed: 17996706
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.08.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QW9, 2QWL, 2QWM, 2QWN, 2QWO, 2QWP, 2QWQ, 2QWR - PubMed Abstract:
The many protein processing reactions of the ATP-hydrolyzing Hsp70s are regulated by J cochaperones, which contain J domains that stimulate Hsp70 ATPase activity and accessory domains that present protein substrates to Hsp70s. We report the structure of a J domain complexed with a J responsive portion of a mammalian Hsp70. The J domain activates ATPase activity by directing the linker that connects the Hsp70 nucleotide binding domain (NBD) and substrate binding domain (SBD) toward a hydrophobic patch on the NBD surface. Binding of the J domain to Hsp70 displaces the SBD from the NBD, which may allow the SBD flexibility to capture diverse substrates. Unlike prokaryotic Hsp70, the SBD and NBD of the mammalian chaperone interact in the ADP state. Thus, although both nucleotides and J cochaperones modulate Hsp70 NBD:linker and NBD:SBD interactions, the intrinsic persistence of those interactions differs in different Hsp70s and this may optimize their activities for different cellular roles.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX 78229-3900, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: