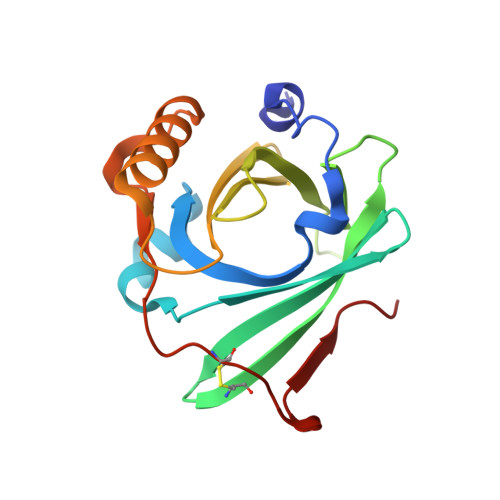
Crystal structure of complement protein C8gamma in complex with a peptide containing the C8gamma binding site on C8alpha: Implications for C8gamma ligand binding.
Lovelace, L.L., Chiswell, B., Slade, D.J., Sodetz, J.M., Lebioda, L.(2008) Mol Immunol 45: 750-756
- PubMed: 17692377
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.06.359
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QOS - PubMed Abstract:
Human C8 is one of five complement components (C5b, C6, C7, C8 and C9) that interact to form the cytolytic membrane attack complex. It contains three genetically distinct subunits; C8alpha and C8gamma form a disulfide-linked C8alpha-gamma heterodimer that is noncovalently associated with C8beta. The C8alpha subunit is homologous to C8beta, C6, C7 and C9 and together they form the MAC family of proteins. By contrast, C8gamma is the only lipocalin in the complement system. Like other lipocalins, it has a core beta-barrel structure forming a calyx with a distinct binding pocket for a small and as yet unidentified ligand. The binding site on C8alpha for C8gamma was previously localized to a 19-residue segment which contains an insertion (indel) that is unique to C8alpha. Included in the indel is C8alpha Cys 164 which links to Cys 40 in C8gamma. In the present study, C8gamma containing a C40A substitution was co-crystallized with a synthetic indel peptide containing the equivalent of a C8alpha C164A substitution. The X-ray crystal structure shows that the indel peptide completely fills the upper portion of the putative C8gamma ligand binding pocket and is in contact with all four loops at the calyx entrance. The lower part of the C8gamma cavity is either unoccupied or contains disordered solvent. The validity of the structure is supported by the spatial arrangement of C8alpha Ala 164 in the peptide and C8gamma Ala 40, which are within disulfide-bonding distance of each other. Corresponding studies in solution indicate the C8gamma ligand binding site is also occupied by the indel segment of C8alpha in whole C8. These results suggest a role for C8alpha in regulating access to the putative C8gamma ligand binding site.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and School of Medicine, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC 29208, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: