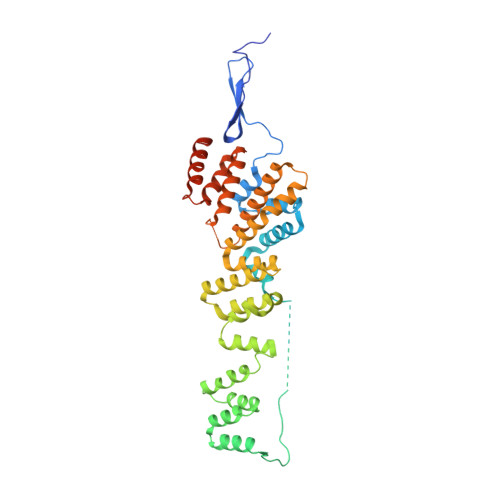
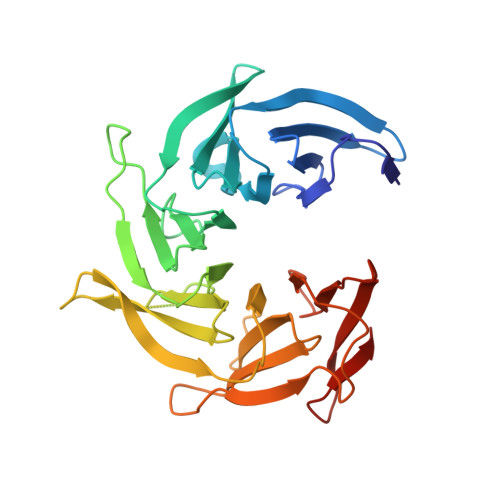
Structure and Organization of Coat Proteins in the COPII Cage.
Fath, S., Mancias, J.D., Bi, X., Goldberg, J.(2007) Cell 129: 1325-1336
- PubMed: 17604721
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PM6, 2PM7, 2PM9 - PubMed Abstract:
COPII-coated vesicles export newly synthesized proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. The COPII coat consists of the Sec23/24-Sar1 complex that selects cargo and the Sec13/31 assembly unit that can polymerize into an octahedral cage and deform the membrane into a bud. Crystallographic analysis of the assembly unit reveals a 28 nm long rod comprising a central alpha-solenoid dimer capped by two beta-propeller domains at each end. We construct a molecular model of the COPII cage by fitting Sec13/31 crystal structures into a recently determined electron microscopy density map. The vertex geometry involves four copies of the Sec31 beta-propeller that converge through their axial ends; there is no interdigitation of assembly units of the kind seen in clathrin cages. We also propose that the assembly unit has a central hinge-an arrangement of interlocked alpha-solenoids-about which it can bend to adapt to cages of variable curvature.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute and the Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10021, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: