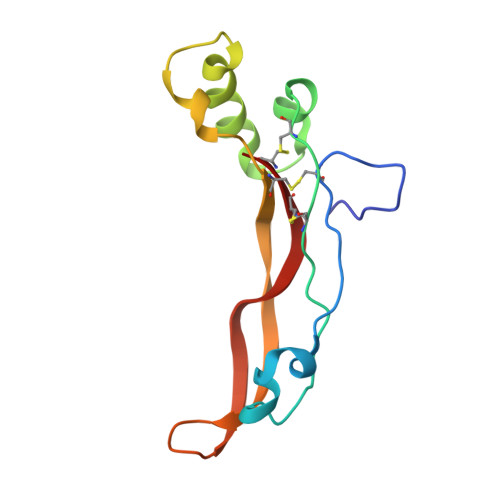
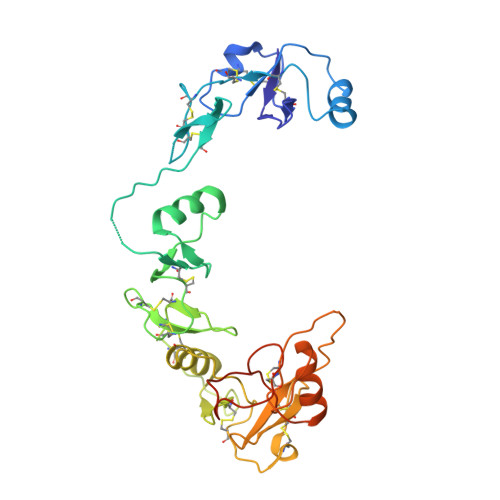
Structural and biophysical coupling of heparin and activin binding to follistatin isoform functions.
Lerch, T.F., Shimasaki, S., Woodruff, T.K., Jardetzky, T.S.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 15930-15939
- PubMed: 17409095
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M700737200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2P6A - PubMed Abstract:
Follistatin (FS) regulates transforming growth factor-beta superfamily ligands and is necessary for normal embryonic and ovarian follicle development. Follistatin is expressed as two splice variants (FS288 and FS315). Previous studies indicated differences in heparin binding between FS288 and FS315, potentially influencing the physiological functions and locations of these isoforms. We have determined the structure of the FS315-activin A complex and quantitatively compared heparin binding by the two isoforms. The FS315 complex structure shows that both isoforms inhibit activin similarly, but FS315 exhibits movements within follistatin domain 3 (FSD3) apparently linked to binding of the C-terminal extension. Surprisingly, the binding affinities of FS288 and FS315 for heparin are similar at lower ionic strengths with FS315 binding decreasing more sharply as a function of salt concentration. When bound to activin, FS315 binds heparin similarly to the FS288 isoform, consistent with the structure of the complex, in which the acidic residues of the C-terminal extension cannot interact with the heparin-binding site. Activin-induced binding of heparin is unique to the FS315 isoform and may stimulate clearance of FS315 complexes.
- Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Cell Biology, Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois 60208, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: