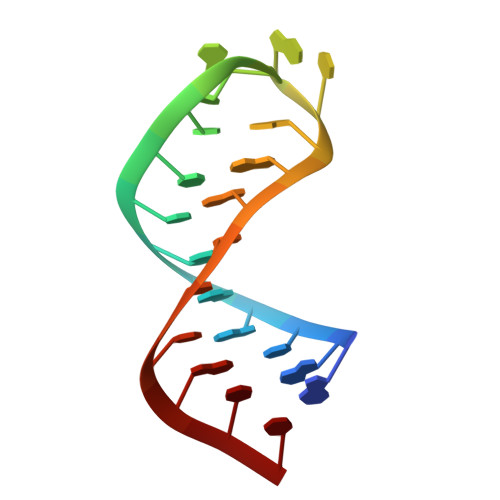
Solution structure and metal ion binding sites of the human CPEB3 ribozyme's P4 domain.
Skilandat, M., Rowinska-Zyrek, M., Sigel, R.K.(2014) J Biol Inorg Chem 19: 903-912
- PubMed: 24652468
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-014-1125-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2M5U - PubMed Abstract:
Three ribozymes are known to occur in humans, the CPEB3 ribozyme, the CoTC ribozyme, and the hammerhead ribozyme. Here, we present the NMR solution structure of a well-conserved motif within the CPEB3 ribozyme, the P4 domain. In addition, we discuss the binding sites and impact of Mg(2+) and [Co(NH3)6](3+), a spectroscopic probe for [Mg(H2O)6](2+), on the structure. The well-defined P4 region is a hairpin closed with a UGGU tetraloop that shows a distinct electrostatic surface potential and a characteristic, strongly curved backbone trajectory. The P4 hairpin contains two specific Mg(2+) binding sites: one outer-sphere binding site close to the proposed CPEB3 ribozyme active site with potential relevance for maintaining a compact fold of the ribozyme core, and one inner-sphere binding site, probably stabilizing the tetraloop structure. The structure of the tetraloop resembles an RNase III recognition structure, as previously described for an AGUU tetraloop. The detailed knowledge of the P4 domain and its metal ion binding preferences thus brings us closer to understanding the importance of Mg(2+) binding for the CPEB3 ribozyme's fold and function in the cell.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Zurich, Winterthurerstrasse 190, 8057, Zurich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: