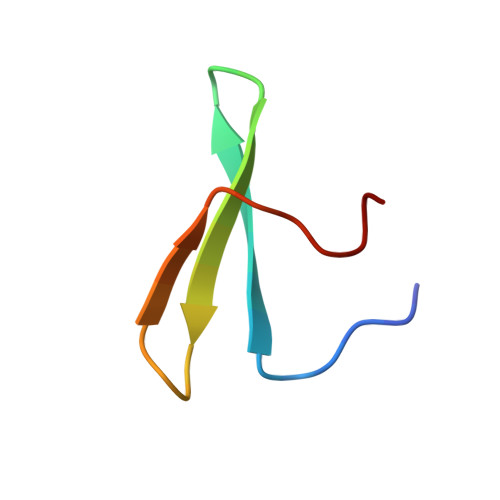
Structural Basis for the Versatile Interactions of Smad7 with Regulator WW Domains in TGF-beta Pathways.
Aragon, E., Goerner, N., Xi, Q., Gomes, T., Gao, S., Massague, J., Macias, M.J.(2012) Structure 20: 1726-1736
- PubMed: 22921829
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.07.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LTV, 2LTW, 2LTX, 2LTY, 2LTZ - PubMed Abstract:
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and BMP signaling is mediated by Smads 1-5 (R-Smads and Co-Smads) and inhibited by Smad7, a major hub of regulation of TGF-β and BMP receptors by negative feedback and antagonistic signals. The transcription coactivator YAP and the E3 ubiquitin ligases Smurf1/2 and Nedd4L target R-Smads for activation or degradation, respectively. Pairs of WW domain in these regulators bind PY motifs and adjacent CDK/MAPK and GSK3 phosphorylation sites in R-Smads in a selective and regulated manner. In contrast, here we show that Smad7 binds YAP, Smurf1, Smurf2, and Nedd4L constitutively, the binding involving a PY motif in Smad7 and no phosphorylation. We also provide a structural basis for how regulators that use WW domain pairs for selective interactions with R-Smads, resort to one single versatile WW domain for binding Smad7 to centralize regulation in the TGF-β and BMP pathways.
- Structural and Computational Biology Programme, Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Baldiri Reixac 10-12, 08028 Barcelona, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: