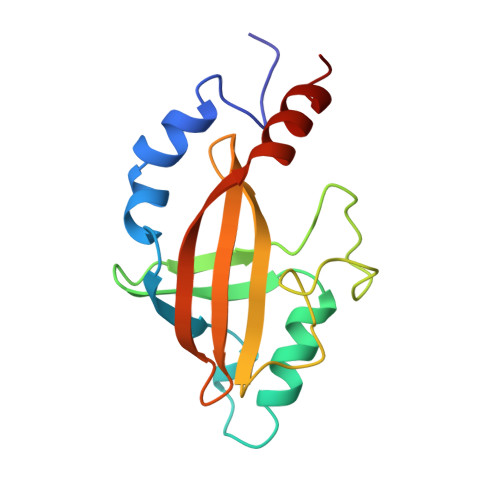
Solution structure of core binding factor beta and map of the CBF alpha binding site.
Huang, X., Peng, J.W., Speck, N.A., Bushweller, J.H.(1999) Nat Struct Biol 6: 624-627
- PubMed: 10404216
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/10670
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JHB - PubMed Abstract:
The core binding factor beta subunit (CBF beta) is the non-DNA binding subunit of the core-binding factors, transcription factors essential for multiple developmental processes including hematopoiesis and bone development. Chromosomal translocations involving the human CBFB gene are associated with a large percentage of human leukemias. The N-terminal 141 amino acids of CBF beta contains the heterodimerization domain for the DNA-binding CBF alpha subunits, and is sufficient for CBF beta function in vivo. Here we present the high-resolution solution structure of the CBF beta heterodimerization domain. It is a novel alpha/beta structure consisting of two three-stranded beta-sheets packed on one another in a sandwich arrangement, with four peripheral alpha-helices. The CBF alpha binding site on CBF beta has been mapped by chemical shift perturbation analysis.
- Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville 22906, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: