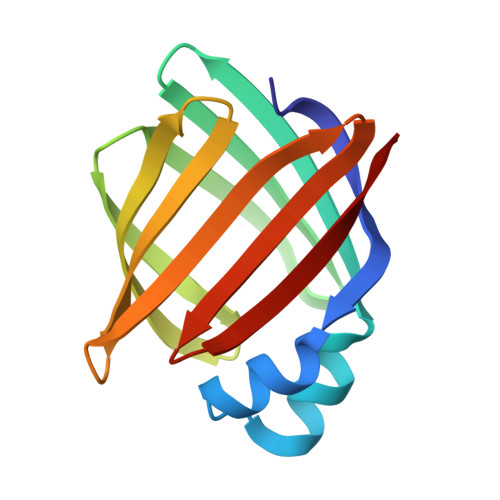
Crystal structure of rat intestinal fatty-acid-binding protein. Refinement and analysis of the Escherichia coli-derived protein with bound palmitate.
Sacchettini, J.C., Gordon, J.I., Banaszak, L.J.(1989) J Mol Biology 208: 327-339
- PubMed: 2671390
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(89)90392-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IFB - PubMed Abstract:
Rat intestinal fatty-acid-binding protein (I-FABP) is a small (15,124 Mr) cytoplasmic polypeptide that binds long-chain fatty acids in a non-covalent fashion. I-FABP is a member of a family of intracellular binding proteins that are thought to participate in the uptake, transport and/or metabolic targeting of hydrophobic ligands. The crystal structure of Escherichia coli-derived rat I-FABP with a single molecule of bound palmitate has been refined to 2 A resolution using a combination of least-squares methods, energy refinement and molecular dynamics. The combined methods resulted in a model with a crystallographic R-factor of 17.8% (7775 reflections, sigma greater than 2.0), root-mean-square bond length deviation of 0.009 A and root-mean-square bond angle deviation of 2.85 degrees. I-FABP contains ten antiparallel beta-strands organized into two approximately orthogonal, beta-sheets. The hydrocarbon tail of its single C16:0 ligand is present in a well-ordered, distinctively bent conformation. The carboxylate group of the fatty acid is located in the interior of I-FABP and forms a unique "quintet" of electrostatic interactions involving Arg106; Gln 115, and two solvent molecules. The hydrocarbon tail is bent with a slight left-handed helical twist from the carboxylate group to C-16. The bent methylene chain resides in a "cradle" formed by the side-chains of hydrophobic, mainly aromatic, amino acid residues. The refined molecular model of holo-I-FABP suggests several potential locations for entry and exiting of the fatty acid.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO 63110.
Organizational Affiliation: