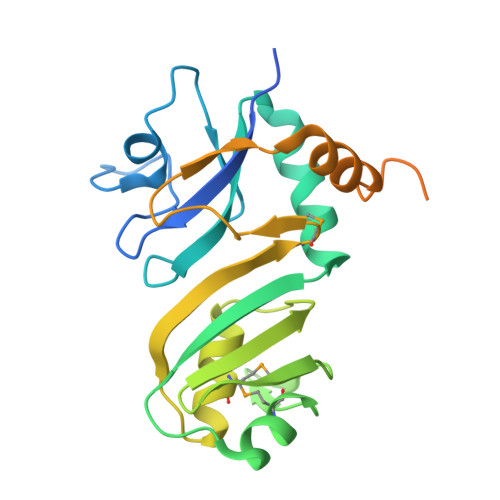
Domain Organization and Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of E.coli RluF, a Pseudouridine Synthase that Acts on 23S rRNA
Sunita, S., Zhenxing, H., Swaathi, J., Cygler, M., Matte, A., Sivaraman, J.(2006) J Mol Biology 359: 998-1009
- PubMed: 16712869
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.04.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2GML - PubMed Abstract:
Pseudouridine synthases catalyze the isomerization of uridine to pseudouridine (Psi) in rRNA and tRNA. The pseudouridine synthase RluF from Escherichia coli (E.C. 4.2.1.70) modifies U2604 in 23S rRNA, and belongs to a large family of pseudouridine synthases present in all kingdoms of life. Here we report the domain architecture and crystal structure of the catalytic domain of E.coli RluF at 2.6A resolution. Limited proteolysis, mass spectrometry and N-terminal sequencing indicate that RluF has a distinct domain architecture, with the catalytic domain flanked at the N and C termini by additional domains connected to it by flexible linkers. The structure of the catalytic domain of RluF is similar to those of RsuA and TruB. RluF is a member of the RsuA sequence family of Psi-synthases, along with RluB and RluE. Structural comparison of RluF with its closest structural homologues, RsuA and TruB, suggests possible functional roles for the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of RluF.
- Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, 14 Science Drive, Singapore, Singapore 117543.
Organizational Affiliation: