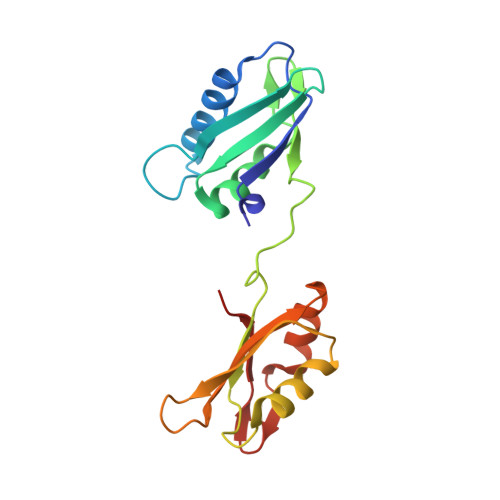
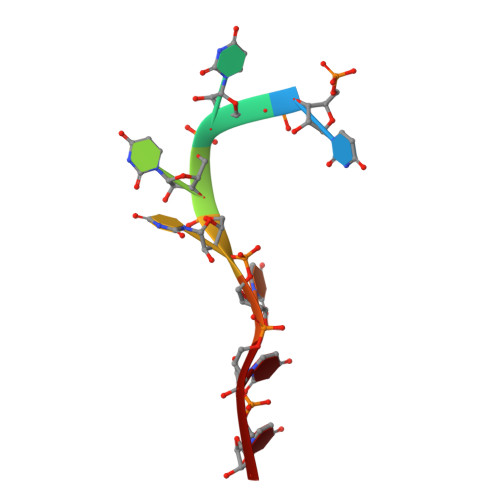
Structural basis of polypyrimidine tract recognition by the essential splicing factor U2AF65.
Sickmier, E.A., Frato, K.E., Paranawithana, S., Shen, H., Green, M.R., Kielkopf, C.L.(2006) Mol Cell 23: 49-59
- PubMed: 16818232
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.025
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2G4B - PubMed Abstract:
The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor, U2AF(65), guides the early stages of splice site choice by recognizing a polypyrimidine (Py) tract consensus sequence near the 3' splice site. Since Py tracts are relatively poorly conserved in higher eukaryotes, U2AF(65) is faced with the problem of specifying uridine-rich sequences, yet tolerating a variety of nucleotide substitutions found in natural Py tracts. To better understand these apparently contradictory RNA binding characteristics, the X-ray structure of the U2AF(65) RNA binding domain bound to a Py tract composed of seven uridines has been determined at 2.5 A resolution. Specific hydrogen bonds between U2AF(65) and the uracil bases provide an explanation for polyuridine recognition. Flexible side chains and bound water molecules form the majority of the base contacts and potentially could rearrange when the U2AF(65) structure adapts to different Py tract sequences. The energetic importance of conserved residues for Py tract binding is established by analysis of site-directed mutant U2AF(65) proteins using surface plasmon resonance.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland 21205, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: