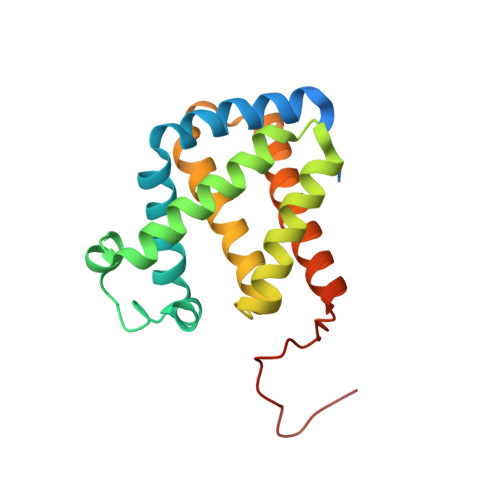
High-resolution structure of human cytoglobin: identification of extra N- and C-termini and a new dimerization mode.
Makino, M., Sugimoto, H., Sawai, H., Kawada, N., Yoshizato, K., Shiro, Y.(2006) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 62: 671-677
- PubMed: 16699195
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444906013813
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DC3 - PubMed Abstract:
Cytoglobin (Cgb) is a recently discovered member of the vertebrate haem-containing globin family. The structure of a new crystal form of wild-type human Cgb (space group C2) was determined at a resolution of 1.68 Angstrom. The results show the presence of an additional helix in the N-terminal residues (4-20) prior to the A helix and an ordered loop structure in the C-terminal region (168-188), while these extended peptides were invisible owing to disorder in the previously reported structures using a P3(2)21 crystal at a resolution of 2.4 Angstrom. A detailed comparison of the two crystal structures shows differences in the conformation of the residues (i.e. Arg84) in the haem environment owing to a different dimeric arrangement.
- Biometal Science Laboratory, Harima Institute, RIKEN SPring-8 Center, Harima Institute, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: