Crystal Structure and Mechanism of Tripeptidyl Activity of Prolyl Tripeptidyl Aminopeptidase from Porphyromonas gingivalis
Ito, K., Nakajima, Y., Xu, Y., Yamada, N., Onohara, Y., Ito, T., Matsubara, F., Kabashima, T., Nakayama, K., Yoshimoto, T.(2006) J Mol Biology 362: 228-240
- PubMed: 16914159
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.083
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D5L, 2DCM - PubMed Abstract:
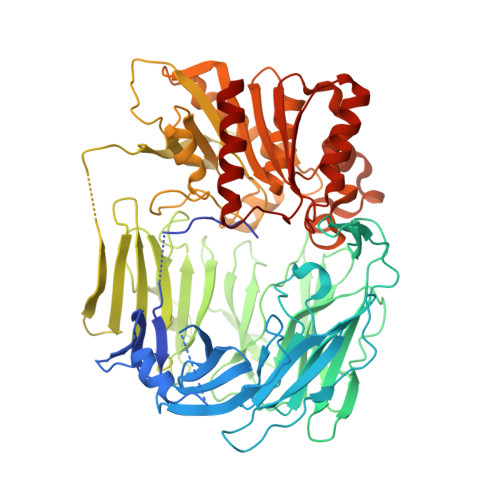
The crystal structure of prolyl tripeptidyl aminopeptidase from Porphyromonas gingivalis was determined. Prolyl tripeptidyl aminopeptidase consists of beta-propeller and catalytic domains, and a large cavity between the domains; this structure is similar to dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV. A catalytic triad (Ser603, His710, and Asp678) was located in the catalytic domain; this triad was virtually identical to that of the enzymes belonging to the prolyl oligopeptidase family. The structure of an inactive S603A mutant enzyme complexed with a substrate was also determined. The pyrrolidine ring of the proline residue appeared to fit into a hydrophobic pocket composed of Tyr604, Val629, Trp632, Tyr635, Tyr639, Val680, and Val681. There were characteristic differences in the residues of the beta-propeller domain, and these differences were related to the substrate specificity of tripeptidyl activity. The N-terminal amino group was recognized by salt bridges, with two carboxyl groups of Glu205 and Glu206 from a helix in dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV. In prolyl tripeptidyl aminopeptidase, however, the Glu205 (located in the loop) and Glu636 were found to carry out this function. The loop structure provides sufficient space to accommodate three N-terminal residues (Xaa-Xaa-Pro) of substrates. This is the first report of the structure and substrate recognition mechanism of tripeptidyl peptidase.
- Gradute School of Biomedical Sciences, Nagasaki University 1-14 Bunkyo-machi, Nagasaki 852-8521, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: