Structural basis for NHERF recognition by ERM proteins
Terawaki, S., Maesaki, R., Hakoshima, T.(2006) Structure 14: 777-789
- PubMed: 16615918
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2006.01.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D10, 2D11 - PubMed Abstract:
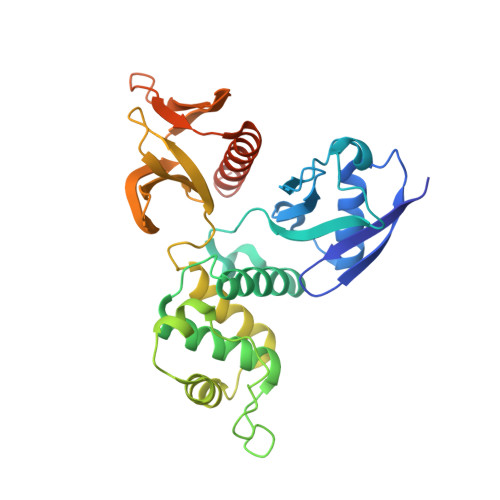
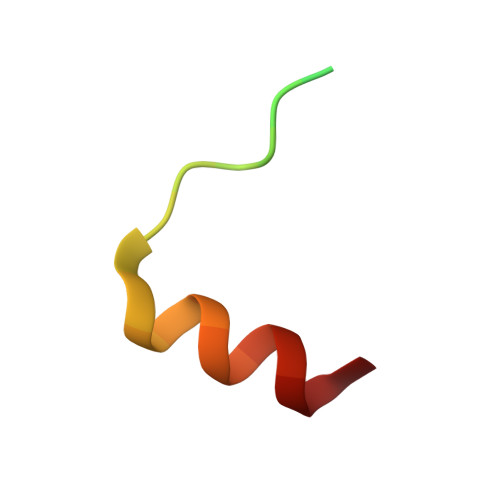
The Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF) is a key adaptor protein involved in the anchoring of ion channels and receptors to the actin cytoskeleton through binding to ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) proteins. NHERF binds the FERM domain of ERM proteins, although NHERF has no signature Motif-1 sequence for FERM binding found in adhesion molecules. The crystal structures of the radixin FERM domain complexed with the NHERF-1 and NHERF-2 C-terminal peptides revealed a peptide binding site of the FERM domain specific for the 13 residue motif MDWxxxxx(L/I)Fxx(L/F) (Motif-2), which is distinct from Motif-1. This Motif-2 forms an amphipathic alpha helix for hydrophobic docking to subdomain C of the FERM domain. This docking causes induced-fit conformational changes in subdomain C and affects binding to adhesion molecule peptides, while the two binding sites are not overlapped. Our studies provide structural paradigms for versatile ERM linkages between membrane proteins and the cytoskeleton.
- Structural Biology Laboratory, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma, Nara 630-0192, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: