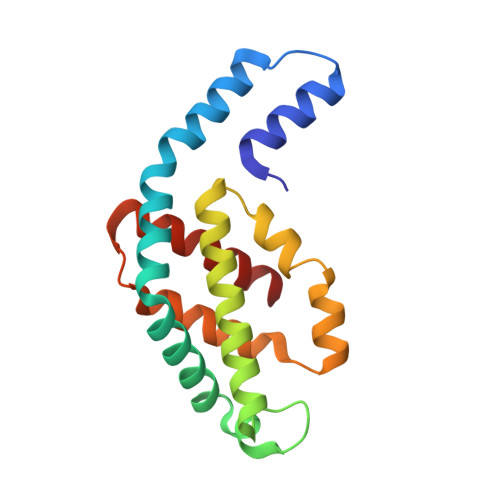
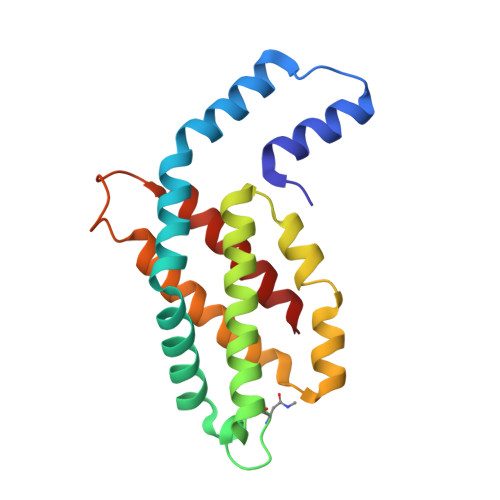
The Structure at 2 A Resolution of Phycocyanin from Gracilaria Chilensis and the Energy Transfer Network in a Pc-Pc Complex.
Contreras-Martel, C., Matamala, A., Bruna, C., Poo-Caama, G., Almonacid, D., Figueroa, M., Martinez-Oyanedel, J., Bunster, M.(2007) Biophys Chem 125: 388
- PubMed: 17118524
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2006.09.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BV8 - PubMed Abstract:
Phycocyanin is a phycobiliprotein involved in light harvesting and conduction of light to the reaction centers in cyanobacteria and red algae. The structure of C-phycocyanin from Gracilaria chilensis was solved by X-ray crystallography at 2.0 A resolution in space group P2(1). An interaction model between two PC heterohexamers was built, followed by molecular dynamic refinement. The best model showed an inter-hexamer rotation of 23 degrees . The coordinates of a PC heterohexamer (alphabeta)(6) and of the PC-PC complex were used to perform energy transfer calculations between chromophores pairs using the fluorescence resonance energy transfer approach (FRET). Two main intra PC ((I)beta(3)(82)-->(I)alpha(1)(84)-->(I)alpha(5)(84)-->(I)beta(6)(82) and (I)beta(3)(153)-->(I)beta(5)(153)) and two main inter PC ((I)beta(6)(82)-->(II)beta(3)(82) and (I)beta(5)(153)-->(II)beta(3)(153)) pathways were proposed based on the values of the energy transfer constants calculated for all the chromophore pairs in the hexamer and in the complex.
- Institut de Biologie Structurale, CEA-CNRS-UJF, Grenoble, France.
Organizational Affiliation: