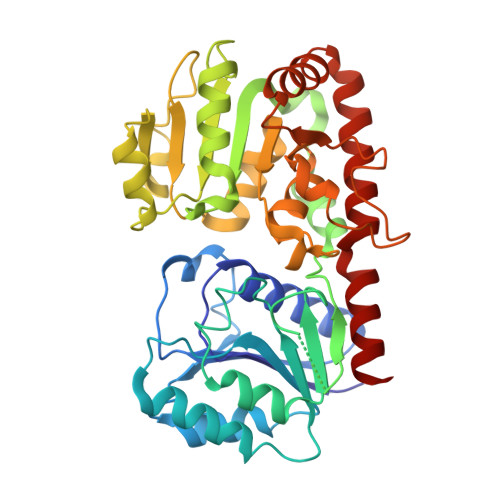
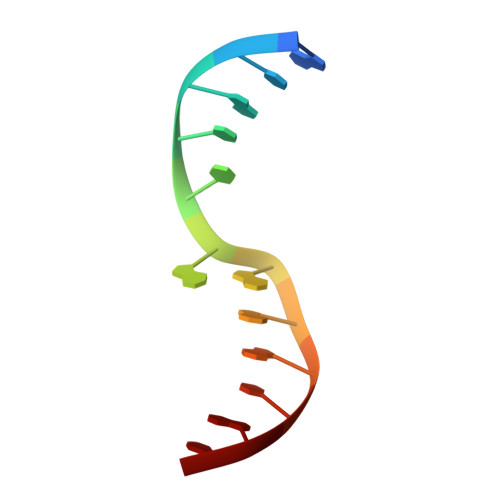
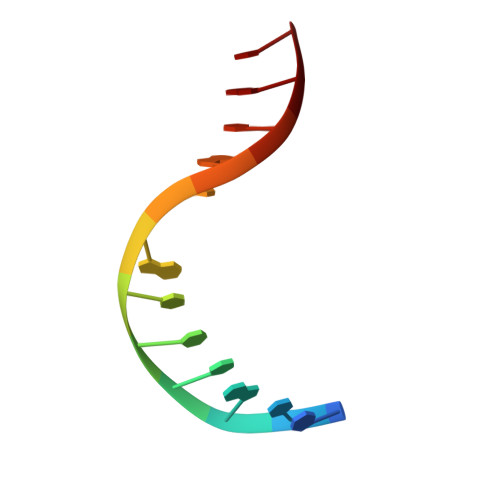
Structural evidence of a passive base-flipping mechanism for AGT, an unusual GT-B glycosyltransferase.
Lariviere, L., Sommer, N., Morera, S.(2005) J Mol Biology 352: 139-150
- PubMed: 16081100
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XV5, 1Y6F, 1Y6G, 1Y8Z, 1YA6 - PubMed Abstract:
The Escherichia coli T4 bacteriophage uses two glycosyltransferases to glucosylate and thus protect its DNA: the retaining alpha-glucosyltransferase (AGT) and the inverting beta-glucosyltransferase (BGT). They glucosylate 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine (5-HMC) bases of duplex DNA using UDP-glucose as the sugar donor to form an alpha-glucosidic linkage and a beta-glucosidic linkage, respectively. Five structures of AGT have been determined: a binary complex with the UDP product and four ternary complexes with UDP or UDP-glucose and oligonucleotides containing an A:G, HMU:G (hydroxymethyl uracyl) or AP:G (apurinic/apyrimidinic) mismatch at the target base-pair. AGT adopts the GT-B fold, one of the two folds known for GTs. However, while the sugar donor binding mode is classical for a GT-B enzyme, the sugar acceptor binding mode is unexpected and breaks the established consensus: AGT is the first GT-B enzyme that predominantly binds both the sugar donor and acceptor to the C-terminal domain. Its active site pocket is highly similar to four retaining GT-B glycosyltransferases (trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, glycogen synthase, glycogen and maltodextrin phosphorylases) strongly suggesting a common evolutionary origin and catalytic mechanism for these enzymes. Structure-guided mutagenesis and kinetic analysis do not permit identification of a nucleophile residue responsible for a glycosyl-enzyme intermediate for the classical double displacement mechanism. Interestingly, the DNA structures reveal partially flipped-out bases. They provide evidence for a passive role of AGT in the base-flipping mechanism and for its specific recognition of the acceptor base.
- Laboratoire d'Enzymologie et Biochimie Structurales, UPR 9063 CNRS, Bât.34, 91198-Gif-sur-Yvette, France.
Organizational Affiliation: