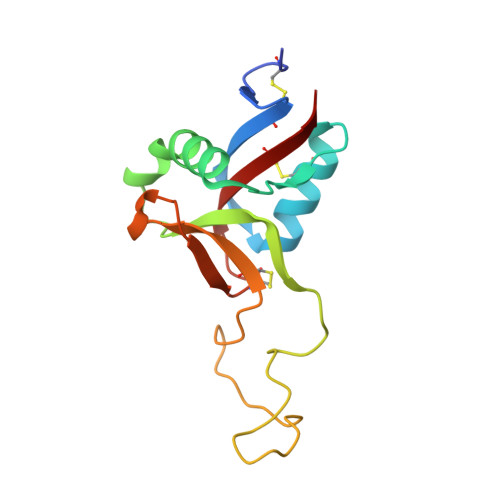
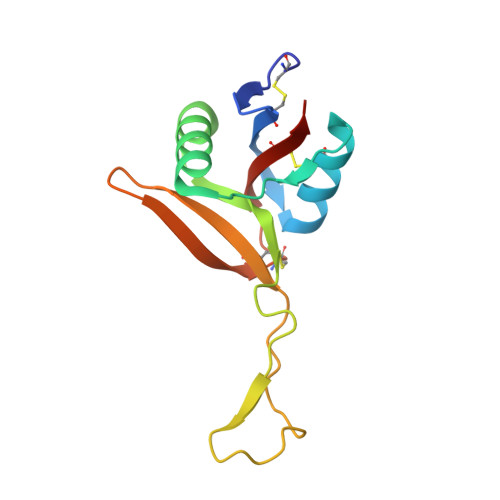
Structural characterization of EMS16, an Antagonist of collagen receptor (GPIa/IIa) from the venom of Echis multisquamatus
Horii, K., Okuda, D., Morita, T., Mizuno, H.(2003) Biochemistry 42: 12497-12502
- PubMed: 14580195
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi034890h
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1UKM - PubMed Abstract:
Snake venoms contain a number of hemostatically active C-type lectin-like proteins (CLPs), which affect the blood coagulation system, endothelial cells, and platelets. CLPs have broad similarities in structure and possess distinct biological functions. EMS16, a CLP from Echis multisquamatus venom, which is a potent and selective inhibitor of the collagen receptor, glycoprotein Ia/IIa (integrin alpha2beta1), has been used in the present study to examine structure-function relationships in venom CLPs by X-ray crystallography. The structure of EMS16, determined at a resolution of 1.9 A, revealed a heterodimer involved with domain swapping of the central loop as observed in the structures of other CLPs. A part of the glycan was observed and identified as N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) in the electron density map at Asn21 of subunit B, an expected glycosylation site. EMS16 had a unique, positively charged electrostatic potential patch on the concave surface that may qualify as a site for interaction with the I-domain of the glycoprotein Ia/IIa.
- Department of Biochemistry, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, 2-1-2 Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8602, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: