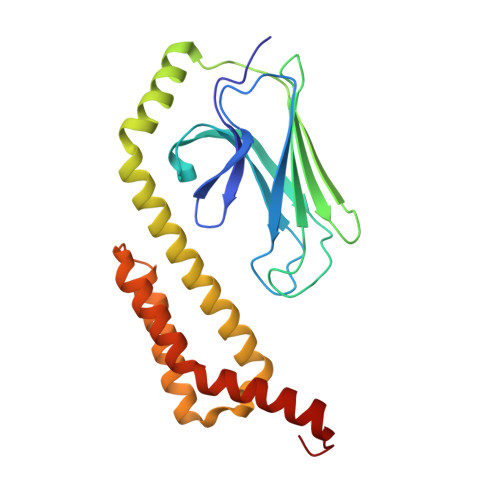
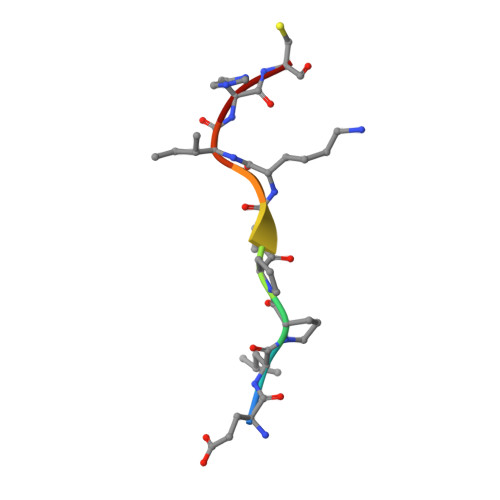
Crystal Structure of the Molecular Chaperone HscA Substrate Binding Domain Complexed with the IscU Recognition Peptide ELPPVKIHC.
Cupp-Vickery, J.R., Peterson, J.C., Ta, D.T., Vickery, L.E.(2004) J Mol Biology 342: 1265-1278
- PubMed: 15351650
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.025
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1U00 - PubMed Abstract:
HscA, a specialized bacterial Hsp70-class molecular chaperone, interacts with the iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein IscU by recognizing a conserved LPPVK sequence motif. We report the crystal structure of the substrate-binding domain of HscA (SBD, residues 389-616) from Escherichia coli bound to an IscU-derived peptide, ELPPVKIHC. The crystals belong to the space group I222 and contain a single molecule in the asymmetric unit. Molecular replacement with the E.coli DnaK(SBD) model was used for phasing, and the HscA(SBD)-peptide model was refined to Rfactor=17.4% (Rfree=21.0%) at 1.95 A resolution. The overall structure of HscA(SBD) is similar to that of DnaK(SBD), although the alpha-helical subdomain (residues 506-613) is shifted up to 10 A relative to the beta-sandwich subdomain (residues 389-498) when compared to DnaK(SBD). The ELPPVKIHC peptide is bound in an extended conformation in a hydrophobic cleft in the beta-subdomain, which appears to be solvent-accessible via a narrow passageway between the alpha and beta-subdomains. The bound peptide is positioned in the reverse orientation of that observed in the DnaK(SBD)-NRLLLTG peptide complex placing the N and C termini of the peptide on opposite sides of the HscA(SBD) relative to the DnaK(SBD) complex. Modeling of the peptide in the DnaK-like forward orientation suggests that differences in hydrogen bonding interactions in the binding cleft and electrostatic interactions involving surface residues near the cleft contribute to the observed directional preference.
- Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697, USA. jvickery@uci.edu
Organizational Affiliation: