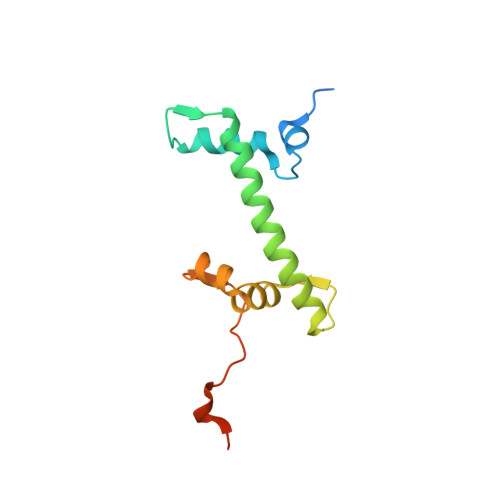
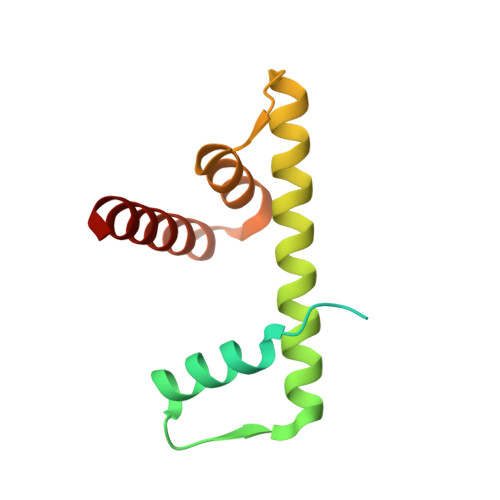
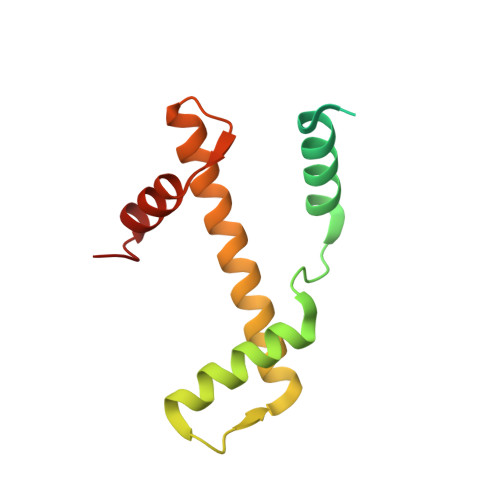
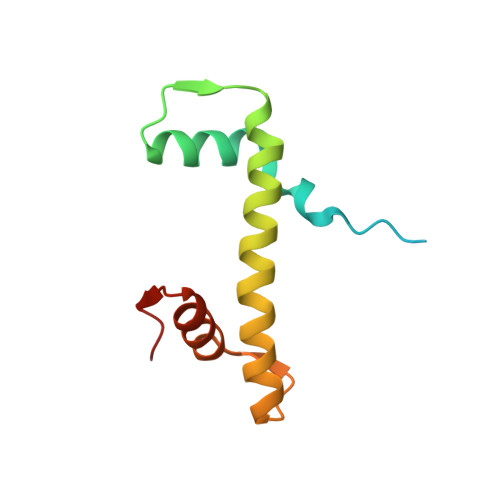
High-resolution structure of the native histone octamer.
Wood, C.M., Nicholson, J.M., Lambert, S.J., Chantalat, L., Reynolds, C.D., Baldwin, J.P.(2005) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 61: 541-545
- PubMed: 16511091
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309105013813
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TZY - PubMed Abstract:
Crystals of native histone octamers (H2A-H2B)-(H4-H3)-(H3'-H4')-(H2B'-H2A') from chick erythrocytes in 2 M KCl, 1.35 M potassium phosphate pH 6.9 diffract X-rays to 1.90 A resolution, yielding a structure with an R(work) value of 18.7% and an Rfree of 22.2%. The crystal space group is P6(5), the asymmetric unit of which contains one complete octamer. This high-resolution model of the histone-core octamer allows further insight into intermolecular interactions, including water molecules, that dock the histone dimers to the tetramer in the nucleosome-core particle and have relevance to nucleosome remodelling. The three key areas analysed are the H2A'-H3-H4 molecular cluster (also H2A-H3'-H4'), the H4-H2B' interaction (also H4'-H2B) and the H2A'-H4 beta-sheet interaction (also H2A-H4'). The latter of these three regions is important to nucleosome remodelling by RNA polymerase II, as it is shown to be a likely core-histone binding site, and its disruption creates an instability in the nucleosome-core particle. A majority of the water molecules in the high-resolution octamer have positions that correlate to similar positions in the high-resolution nucleosome-core particle structure, suggesting that the high-resolution octamer model can be used for comparative studies with the high-resolution nucleosome-core particle.
- School of Biomolecular Sciences, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool L3 3AF, England. c.m.wood@livjm.ac.uk
Organizational Affiliation: