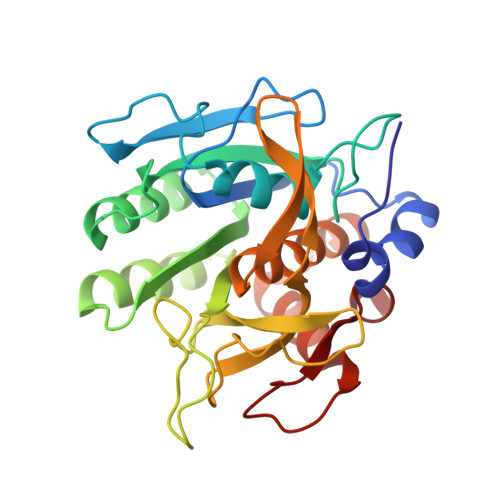
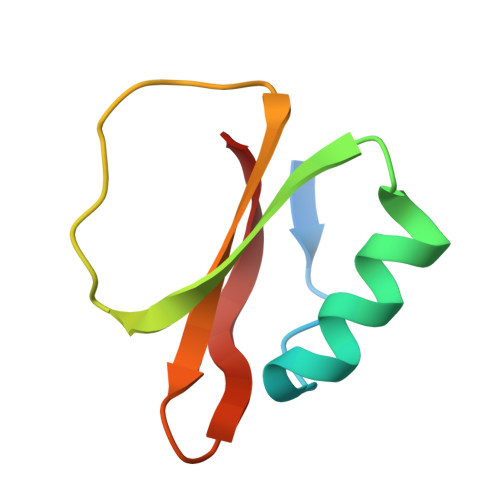
Refined crystal structures of subtilisin novo in complex with wild-type and two mutant eglins. Comparison with other serine proteinase inhibitor complexes.
Heinz, D.W., Priestle, J.P., Rahuel, J., Wilson, K.S., Grutter, M.G.(1991) J Mol Biology 217: 353-371
- PubMed: 1992167
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(91)90549-l
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SBN, 1SIB - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structures of the complexes formed between subtilisin Novo and three inhibitors, eglin c, Arg45-eglin c and Lys53-eglin c have been determined using molecular replacement and difference Fourier techniques and refined at 2.4 A, 2.1 A, and 2.4 A resolution, respectively. The mutants Arg45-eglin c and Lys53-eglin c were constructed by site-directed mutagenesis in order to investigate the inhibitory specificity and stability of eglin c. Arg45-eglin became a potent trypsin inhibitor, in contrast to native eglin, which is an elastase inhibitor. This specificity change was rationalized by comparing the structures of Arg45-eglin and basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and their interactions with trypsin. The residue Arg53, which participates in a complex network of hydrogen bonds formed between the core and the binding loop of eglin c, was replaced with the shorter basic amino acid lysine in the mutant Lys53-eglin. Two hydrogen bonds with Thr44, located in the binding loop, can no longer be formed but are partially restored by a water molecule bound in the vicinity of Lys53. Eglin c in complexes with both subtilisin Novo and subtilisin Carlsberg was crystallized in two different space groups. Comparison of the complexes showed a rigid body rotation for the eglin c core of 11.5 degrees with respect to the enzyme, probably caused by different intermolecular contacts in both crystal forms.
- Pharmaceutical Division, Ciba-Geigy Ltd., Basel, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: