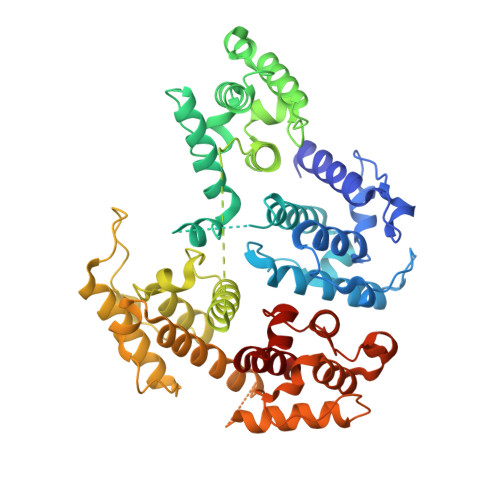
Structure of the actin crosslinking core of fimbrin.
Klein, M.G., Shi, W., Ramagopal, U., Tseng, Y., Wirtz, D., Kovar, D.R., Staiger, C.J., Almo, S.C.(2004) Structure 12: 999-1013
- PubMed: 15274920
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.04.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PXY, 1RT8 - PubMed Abstract:
Filamentous actin is organized into bundles and orthogonal networks by the fimbrin/alpha-actinin superfamily of F-actin crosslinking proteins. The crystal structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana and Schizosaccharomyces pombe fimbrin cores provides the first description of a functional F-actin crosslinking protein and highlights the compact and distinctly asymmetric organization of the fimbrin molecule, in which the two actin binding domains present distinct surfaces to solvent. The mapping of functionally important residues onto the structure affords new insights into the binding process and provides additional constraints which must be accommodated by models for F-actin binding and crosslinking. Most strikingly, this work provides unique insight into the mechanistic features of conditional-lethal mutants and their extragenic suppressors, which highlight conformational and dynamic properties required for fimbrin function. These results underscore the power of jointly considering structural and genetic suppressor data for obtaining unexpected and biologically relevant mechanistic information.
- Department of Biochemistry, Center for Synchrotron Biosciences, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, 1300 Morris Park Avenue, Bronx, NY 10461, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: