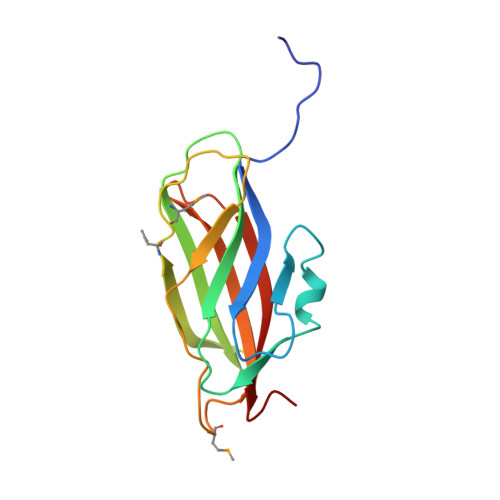
A modulator of rho family G proteins, rhoGDI, binds these G proteins via an immunoglobulin-like domain and a flexible N-terminal arm.
Keep, N.H., Barnes, M., Barsukov, I., Badii, R., Lian, L.Y., Segal, A.W., Moody, P.C., Roberts, G.C.(1997) Structure 5: 623-633
- PubMed: 9195882
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00218-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RHO - PubMed Abstract:
The rho family of small G proteins, including rho, rac and cdc42, are involved in many cellular processes, including cell transformation by ras and the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Additionally, rac has a role in the regulation of phagocyte NADPH oxidase. Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs) of the rhoGDI family bind to these G proteins and regulate their activity by preventing nucleotide dissociation and by controlling their interaction with membranes. We report the structure of rhoGDI, determined by a combination of X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. NMR spectroscopy and selective proteolysis show that the N-terminal 50-60 residues of rhoGDI are flexible and unstructured in solution. The 2.5 A crystal structure of the folded core of rhoGDI, comprising residues 59-204, shows it to have an immunoglobulin-like fold, with an unprecedented insertion of two short beta strands and a 310 helix. There is an unusual pocket between the beta sheets of the immunoglobulin fold which may bind the C-terminal isoprenyl group of rac. NMR spectroscopy shows that the N-terminal arm is necessary for binding rac, although it remains largely flexible even in the complex. The rhoGDI structure is notable for the existence of both a structured and a highly flexible domain, both of which appear to be required for the interaction with rac. The immunoglobulin-like fold of the structured domain is unusual for a cytoplasmic protein. The presence of equivalent cleavage sites in rhoGDI and the closely related D4/Ly-GDI (rhoGDI-2) suggest that proteolytic cleavage between the flexible and structured regions of rhoGDI may have a role in the regulation of the activity of members of this family. There is no detectable similarity between the structure of rhoGDI and the recently reported structure of rabGDI, which performs the same function as rhoGDI for the rab family of small G proteins.
- Department of Medicine, University College London, Rayne Institute, 5 University Street, London, WC1E 6JJ, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: