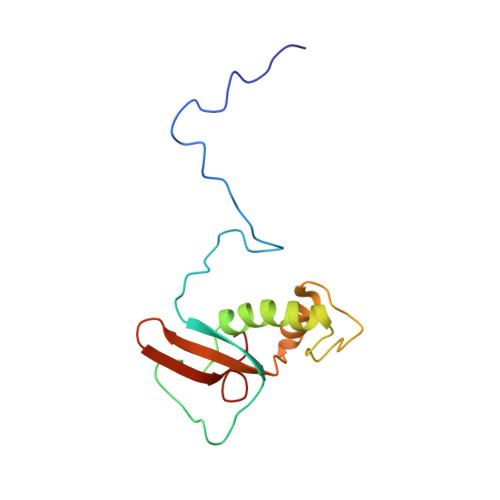
Solution Structure of the Hrpabc14.4 Subunit of Human RNA Polymerases
Del Rio-Portilla, F., Gaskell, A.G., Gilbert, D., Ladias, J.A.A., Wagner, G.(1999) Nat Struct Biol 6: 1039
- PubMed: 10542096
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/14923
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QKL - PubMed Abstract:
The protein hRPABC14.4 is an essential subunit of human RNA polymerases I, II, and III and is required for the transcription of all human nuclear genes. The structure of hRPABC14.4 was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The protein fold comprises a highly conserved central domain forming two antiparallel alpha-helices flanked by the less conserved N- and C-terminal regions forming a five-stranded beta-sandwich. Amino acids from the two helices participate in the generation of a hydrophobic surface area which is conserved in all eukaryotic and archaeal homologous subunits, and likely constitutes a critical macromolecular interaction interface. The hRPABC14.4 structure accounts for mutagenesis results in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and provides a structural working model for elucidating the role of this subunit in the molecular architecture and function of the human nuclear RNA polymerases.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: