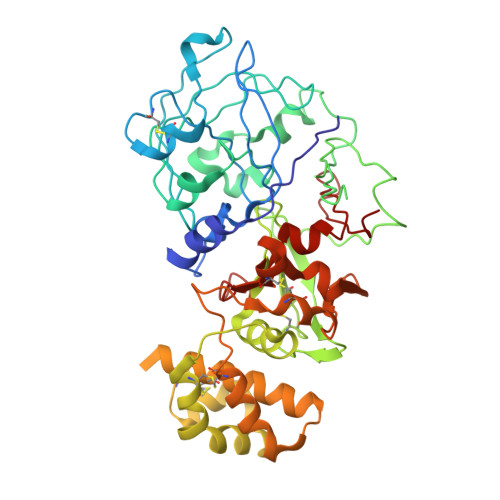
Crystal structure of plant aspartic proteinase prophytepsin: inactivation and vacuolar targeting.
Kervinen, J., Tobin, G.J., Costa, J., Waugh, D.S., Wlodawer, A., Zdanov, A.(1999) EMBO J 18: 3947-3955
- PubMed: 10406799
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.14.3947
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QDM - PubMed Abstract:
We determined at 2.3 A resolution the crystal structure of prophytepsin, a zymogen of a barley vacuolar aspartic proteinase. In addition to the classical pepsin-like bilobal main body of phytepsin, we also traced most of the propeptide, as well as an independent plant-specific domain, never before described in structural terms. The structure revealed that, in addition to the propeptide, 13 N-terminal residues of the mature phytepsin are essential for inactivation of the enzyme. Comparison of the plant-specific domain with NK-lysin indicates that these two saposin-like structures are closely related, suggesting that all saposins and saposin-like domains share a common topology. Structural analysis of prophytepsin led to the identification of a putative membrane receptor-binding site involved in Golgi-mediated transport to vacuoles.
- Protein Structure Section, Macromolecular Structure Laboratory, ABL-Basic Research Program, NCI-Frederick Cancer Research and Development Center, Frederick, MD 21702, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: