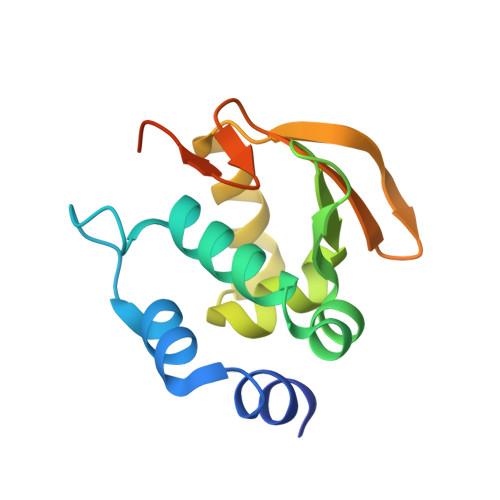
Structural Basis of Core Promoter Recognition in a Primitive Eukaryote
Schumacher, M.A., Lau, A.O.T., Johnson, P.J.(2003) Cell 115: 413-424
- PubMed: 14622596
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00887-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PP7, 1PP8, 1Q87, 1Q88, 1Q89 - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription start site selection in eukaryotes is mediated through combinations of the TATA, initiator (Inr), and downstream promoter elements (DPE). In Trichomonas vaginalis, a parabasalian flagellate thought to represent an ancient eukaryote lineage, the Inr appears to be solely responsible for start site selection and is recognized by the initiator binding protein 39 kDa (IBP39). IBP39 contains an N-terminal Inr binding domain (IBD) connected via a flexible linker to a C-terminal domain (C domain). Here we present crystal structures of the apoIBD and IBD-Inr complexes and the C domain. The IBD structures reveal a winged-helix motif with prokaryotic and eukaryotic features and a scaffold similar to that of ETS-family proteins. The C domain structure and biochemical studies indicate that it interacts with the T. vaginalis RNAP II large subunit C-terminal domain. These data suggest that binding of IBP39 to the Inr directly recruits RNAP II and in this way initiates transcription.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR 97239, USA. schumacm@ohsu.edu
Organizational Affiliation: