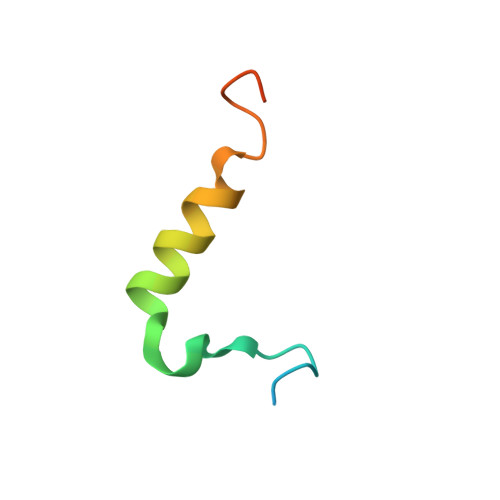
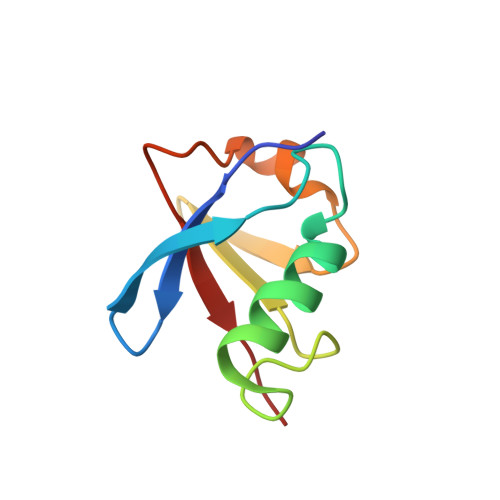
Structural determinants for the binding of ubiquitin-like domains to the proteasome.
Mueller, T.D., Feigon, J.(2003) EMBO J 22: 4634-4645
- PubMed: 12970176
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg467
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1P98, 1P9C, 1P9D - PubMed Abstract:
HHR23A, a protein implicated in nucleotide excision repair, belongs to a class of proteins containing both a ubiquitin-like (Ubl) domain and one or more ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domains, suggesting a role in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway as well. The Ubl domain binds with high affinity to the second ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM) of the S5a subunit of the proteasome. Here we present the solution structures of the HHR23A Ubl domain, the second UIM of S5a (UIM-2), and the Ubl:S5a-UIM-2 complex. The HHR23A Ubl domain is structurally similar to ubiquitin. The S5a UIM forms an alpha-helix with an unexpected hairpin loop that contributes to the binding interface with Ubl. The molecular determinants of the Ubl-proteasome interaction are revealed by analysis of the structures, chemical shift mapping, mutant binding studies and sequence conservation.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, 405 Hilgard Avenue, PO Box 951569, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1569, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: