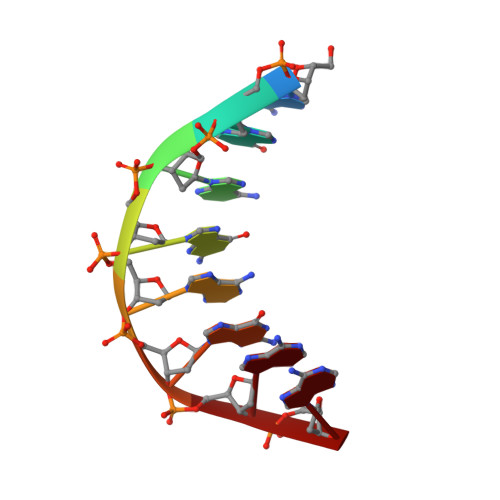
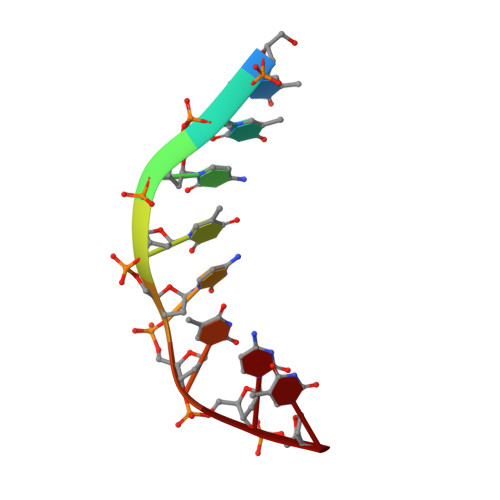
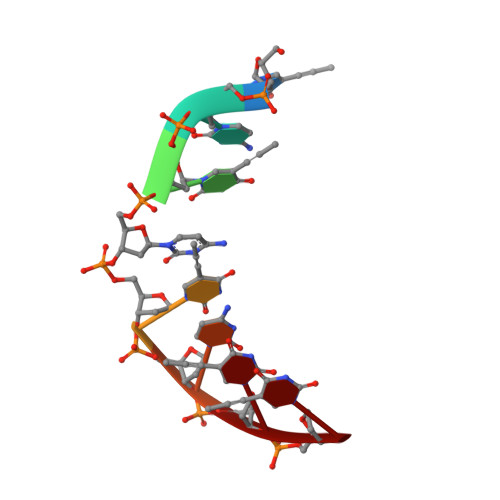
Solution structure of an intramolecular DNA triplex containing 5-(1-propynyl)-2'-deoxyuridine residues in the third strand.
Phipps, A.K., Tarkoy, M., Schultze, P., Feigon, J.(1998) Biochemistry 37: 5820-5830
- PubMed: 9558315
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi972811u
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1P3X - PubMed Abstract:
Incorporation of the modified base 5-(1-propynl)-2'-deoxyuridine (propynylU) in the third strand of a triplex leads to enhanced triplex stabilization. To investigate effects of the propyne nucleotide on triplex structure and the factors underlying the increased stability, we have determined the solution structure of the intramolecular DNA pyrmidine-purine-pyrimdine d(AGAGAGAA-(EG)6-TTCTCTCT-(EG)6-PCPCPCPP) (PDD-EG), which contains 5-(1-propynl)-2'-deoxyuridine (P) in the third strand and hexakis(ethylene glycol) linkers [(EG)6]. The structure was calculated using X-PLOR with distance and dihedral angle restraints obtained from two-dimensional NMR experiments and refined with the direct relaxation matrix method. The structures show that the extended aromatic electron cloud of the propynylU nucleotide stacks well over the 5'-neighboring nucleotides, resulting in increased stabilization. The propynylU nucleotides also affect the overall structure of the triple helix. A comparison of the structure to that of the nonmodified intramolecular DNA triplex of the same sequence, d(AGAGAGAA-(EG)6-TTCTCTCT-(EG)6-TCTCTCTT) (DDD-EG), shows that PDD-EG has a more A-DNA like X displacement and inclination than DDD-EG yet still maintains predominantly S-type sugar puckers as found in DDD-EG and other DNA triplexes.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Molecular Biology Institute, University of California, Los Angeles 90095-1569, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: