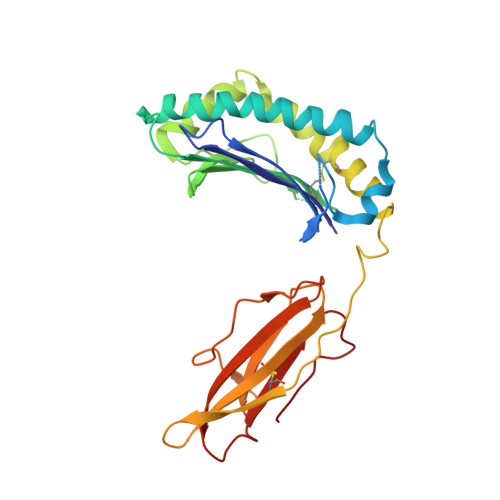
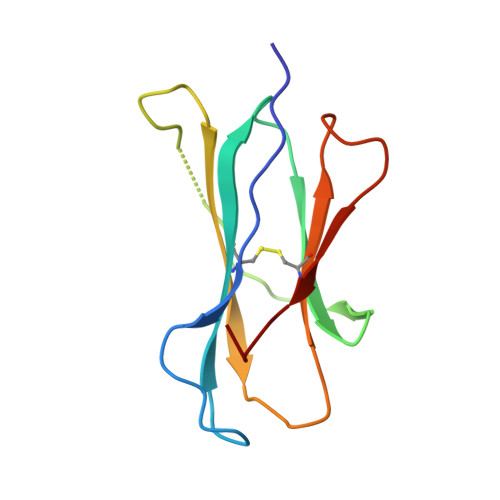
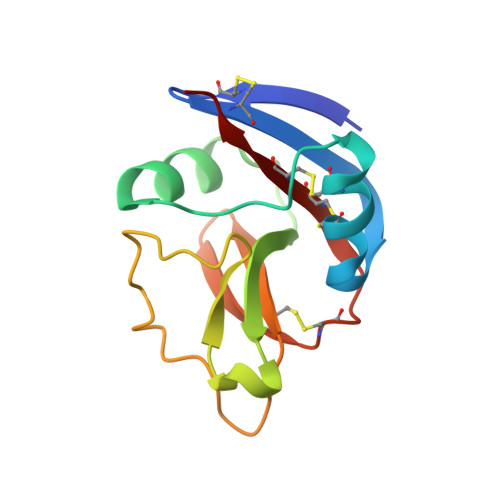
Variable MHC class I engagement by Ly49 natural killer cell receptors demonstrated by the crystal structure of Ly49C bound to H-2K(b).
Dam, J., Guan, R., Natarajan, K., Dimasi, N., Chlewicki, L.K., Kranz, D.M., Schuck, P., Margulies, D.H., Mariuzza, R.A.(2003) Nat Immunol 4: 1213-1222
- PubMed: 14595439
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1P1Z, 1P4L - PubMed Abstract:
The Ly49 family of natural killer (NK) receptors regulates NK cell function by sensing major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I. Ly49 receptors show complex patterns of MHC class I cross-reactivity and, in certain cases, peptide selectivity. To investigate whether specificity differences result from topological differences in MHC class I engagement, we determined the structure of the peptide-selective receptor Ly49C in complex with H-2K(b). The Ly49C homodimer binds two MHC class I molecules in symmetrical way, a mode distinct from that of Ly49A, which binds MHC class I asymmetrically. Ly49C does not directly contact the MHC-bound peptide. In addition, MHC crosslinking by Ly49C was demonstrated in solution. We propose a dynamic model for Ly49-MHC class I interactions involving conformational changes in the receptor, whereby variations in Ly49 dimerization mediate different MHC-binding modes.
- Center for Advanced Research in Biotechnology, W.M. Keck Laboratory for Structural Biology, University of Maryland Biotechnology Institute, 9600 Gudelsky Drive, Rockville, Maryland 20850, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: