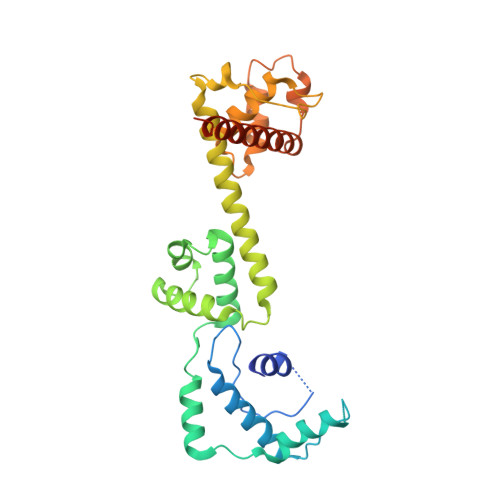
Crystal Structure and Functional Analysis of a Nucleosome Recognition Module of the Remodeling Factor Iswi
Grune, T., Brzeski, J., Eberharter, A., Clapier, C.R., Corona, D.F.V., Becker, P.B., Muller, C.W.(2003) Mol Cell 12: 449
- PubMed: 14536084
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00273-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OFC - PubMed Abstract:
Energy-dependent nucleosome remodeling emerges as a key process endowing chromatin with dynamic properties. However, the principles by which remodeling ATPases interact with their nucleosome substrate to alter histone-DNA interactions are only poorly understood. We have identified a substrate recognition domain in the C-terminal half of the remodeling ATPase ISWI and determined its structure by X-ray crystallography. The structure comprises three domains, a four-helix domain with a novel fold and two alpha-helical domains related to the modules of c-Myb, SANT and SLIDE, which are linked by a long helix. An integrated structural and functional analysis of these domains provides insight into how ISWI interacts with the nucleosomal substrate.
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Grenoble Outstation, B.P. 181, F 38042 Grenoble 9, France.
Organizational Affiliation: