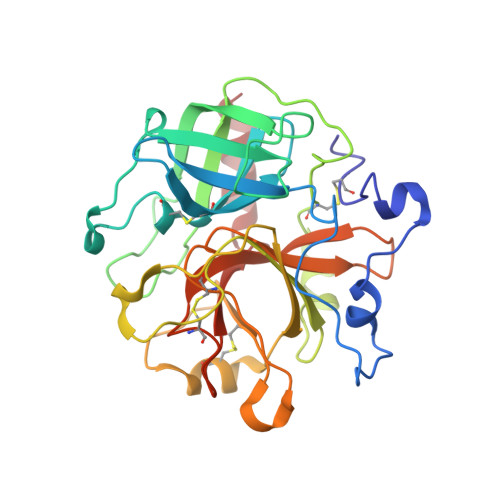
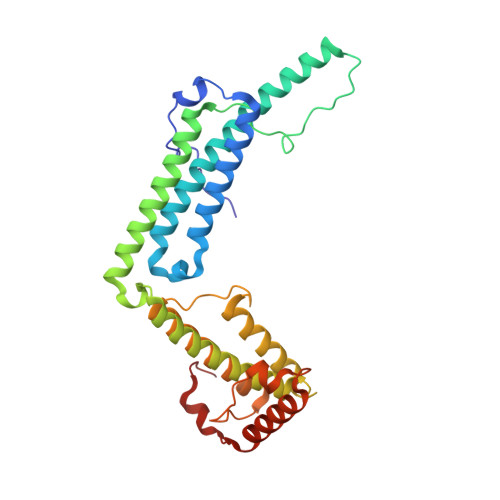
Staphylocoagulase is a prototype for the mechanism of cofactor-induced zymogen activation
Friedrich, R., Panizzi, P., Fuentes-Prior, P., Richter, K., Verhamme, I., Anderson, P.J., Kawabata, S., Huber, R., Bode, W., Bock, P.E.(2003) Nature 425: 535-539
- PubMed: 14523451
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01962
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NU7, 1NU9 - PubMed Abstract:
Many bacterial pathogens secrete proteins that activate host trypsinogen-like enzyme precursors, most notably the proenzymes of the blood coagulation and fibrinolysis systems. Staphylococcus aureus, an important human pathogen implicated in sepsis and endocarditis, secretes the cofactor staphylocoagulase, which activates prothrombin, without the usual proteolytic cleavages, to directly initiate blood clotting. Here we present the 2.2 A crystal structures of human alpha-thrombin and prethrombin-2 bound to a fully active staphylocoagulase variant. The cofactor consists of two domains, each with three-helix bundles; this is a novel fold that is distinct from known serine proteinase activators, particularly the streptococcal plasminogen activator streptokinase. The staphylocoagulase fold is conserved in other bacterial plasma-protein-binding factors and extracellular-matrix-binding factors. Kinetic studies confirm the importance of isoleucine 1 and valine 2 at the amino terminus of staphylocoagulase for zymogen activation. In addition to making contacts with the 148 loop and (pro)exosite I of prethrombin-2, staphylocoagulase inserts its N-terminal peptide into the activation pocket of bound prethrombin-2, allosterically inducing functional catalytic machinery. These investigations demonstrate unambiguously the validity of the zymogen-activation mechanism known as 'molecular sexuality'.
- Abteilung Strukturforschung, Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, D-82152 Martinsried, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: