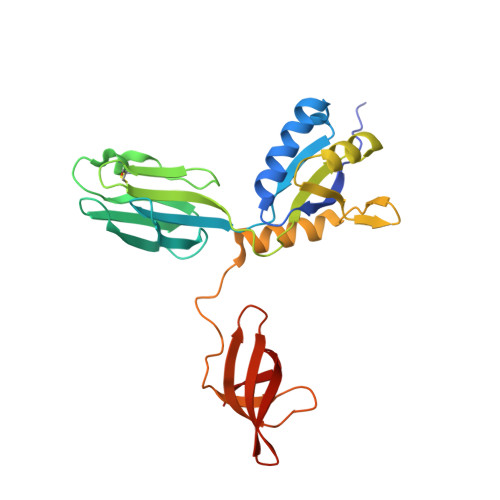
A Spring-Loaded State of NusG in Its Functional Cycle Is Suggested by X-ray Crystallography and Supported by Site-Directed Mutants
Knowlton, J.R., Bubunenko, M., Andrykovitch, M., Guo, W., Routzahn, K.M., Waugh, D.S., Court, D.L., Ji, X.(2003) Biochemistry 42: 2275-2281
- PubMed: 12600194
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0272508
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NPP, 1NPR - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription factor NusG is present in all prokaryotes, and orthologous proteins have also been identified in yeast and humans. NusG contains a 27-residue KOW motif, found in ribosomal protein L24 where it interacts with rRNA. NusG in Escherichia coli (EcNusG) is an essential protein and functions as a regulator of Rho-dependent transcription termination, phage lambda N and rRNA transcription antitermination, and phage HK022 Nun termination. Relative to EcNusG, Aquifex aeolicus NusG (AaNusG) and several other bacterial NusG proteins contain a variable insertion sequence of approximately 70 residues in the central region of the molecule. Recently, crystal structures of AaNusG in space groups P2(1) and I222 have been reported; the authors conclude that there are no conserved dimers among the contacting molecules in the crystals [Steiner, T., Kaiser, J. T., Marinkovic, S., Huber, R., and Wahl, M. C. (2002) EMBO J. 21, 4641-4653]. We have independently determined the structures of AaNusG also in two crystal forms, P2(1) and C222(1), and surprisingly found that AaNusG molecules form domain-swapped dimers in both crystals. Additionally, polymerization is also observed in the P2(1) crystal. A unique "ball-and-socket" junction dominates the intermolecular interactions within both oligomers. We believe that this interaction is a clue to the function of the molecule and propose a spring-loaded state in the functional cycle of NusG. The importance of the ball-and-socket junction for the function of NusG is supported by the functional analysis of site-directed mutants.
- Macromolecular Crystallography Laboratory, National Cancer Institute, P.O. Box B, Frederick, Maryland 21702, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: