X-ray structures of Myc-Max and Mad-Max recognizing DNA: Molecular bases of regulation by proto-oncogenic transcription factors
Nair, S.K., Burley, S.K.(2003) Cell 112: 193-205
- PubMed: 12553908
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01284-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NKP, 1NLW - PubMed Abstract:
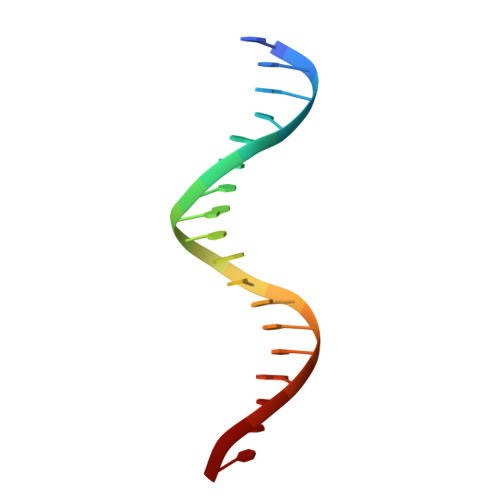
X-ray structures of the basic/helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper (bHLHZ) domains of Myc-Max and Mad-Max heterodimers bound to their common DNA target (Enhancer or E box hexanucleotide, 5'-CACGTG-3') have been determined at 1.9 A and 2.0 A resolution, respectively. E box recognition by these two structurally similar transcription factor pairs determines whether a cell will divide and proliferate (Myc-Max) or differentiate and become quiescent (Mad-Max). Deregulation of Myc has been implicated in the development of many human cancers, including Burkitt's lymphoma, neuroblastomas, and small cell lung cancers. Both quasisymmetric heterodimers resemble the symmetric Max homodimer, albeit with marked structural differences in the coiled-coil leucine zipper regions that explain preferential homo- and heteromeric dimerization of these three evolutionarily related DNA-binding proteins. The Myc-Max heterodimer, but not its Mad-Max counterpart, dimerizes to form a bivalent heterotetramer, which explains how Myc can upregulate expression of genes with promoters bearing widely separated E boxes.
- Laboratories of Molecular Biophysics, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: