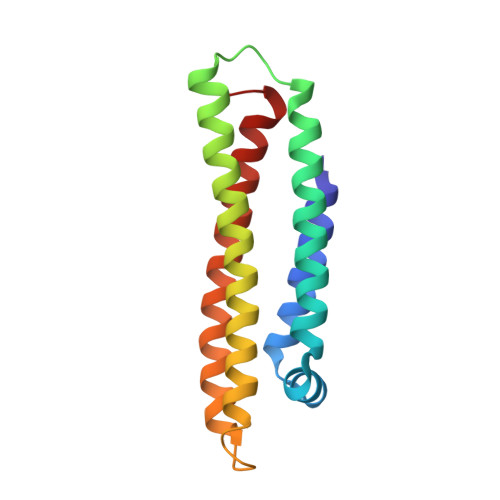
Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E.
Wilson, C., Wardell, M.R., Weisgraber, K.H., Mahley, R.W., Agard, D.A.(1991) Science 252: 1817-1822
- PubMed: 2063194
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2063194
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LPE - PubMed Abstract:
Human apolipoprotein E, a blood plasma protein, mediates the transport and uptake of cholesterol and lipid by way of its high affinity interaction with different cellular receptors, including the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor. The three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of apoE has been determined at 2.5 angstrom resolution by x-ray crystallography. The protein forms an unusually elongated (65 angstroms) four-helix bundle, with the helices apparently stabilized by a tightly packed hydrophobic core that includes leucine zipper-type interactions and by numerous salt bridges on the mostly charged surface. Basic amino acids important for LDL receptor binding are clustered into a surface patch on one long helix. This structure provides the basis for understanding the behavior of naturally occurring mutants that can lead to atherosclerosis.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of California, San Francisco 94143-0448.
Organizational Affiliation: