Solution structure and dynamics of the lipoic acid-bearing domain of human mitochondrial branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex
Chang, C.-F., Chou, H.-T., Chuang, J.L., Chuang, D.T., Huang, T.-h.(2002) J Biological Chem 277: 15865-15873
- PubMed: 11839747
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110952200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1K8M, 1K8O - PubMed Abstract:
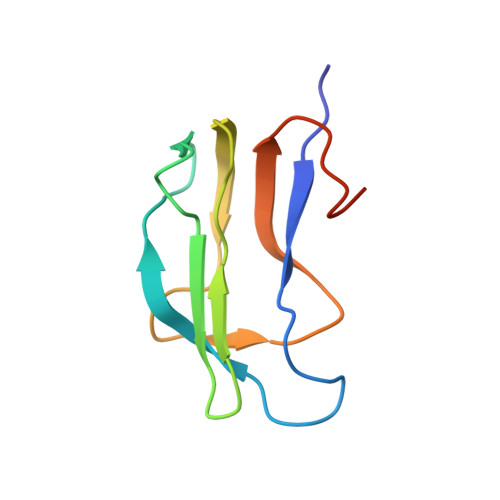
The lipoyl-bearing domain (LBD) of the transacylase (E2) subunit of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex plays a central role in substrate channeling in this mitochondrial multienzyme complex. We have employed multidimensional heteronuclear NMR techniques to determine the structure and dynamics of the LBD of the human branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (hbLBD). Similar to LBD from other members of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase family, the solution structure of hbLBD is a flattened beta-barrel formed by two four-stranded antiparallel beta-sheets. The lipoyl Lys(44) residue resides at the tip of a beta-hairpin comprising a sharp type I beta-turn and the two connecting beta-strands 4 and 5. A prominent V-shaped groove formed by a surface loop, L1, connecting beta 1- and beta 2-strands and the lipoyl lysine beta-hairpin constitutes the functional pocket. We further applied reduced spectral density functions formalism to extract dynamic information of hbLBD from (15)N-T(1), (15)N-T(2), and ((1)H-(15)N) nuclear Overhauser effect data obtained at 600 MHz. The results showed that residues surrounding the lipoyl lysine region comprising the L1 loop and the Lys(44) beta-turn are highly flexible, whereas beta-sheet S1 appears to display a slow conformational exchange process.
- Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan 11529, Republic of China.
Organizational Affiliation: