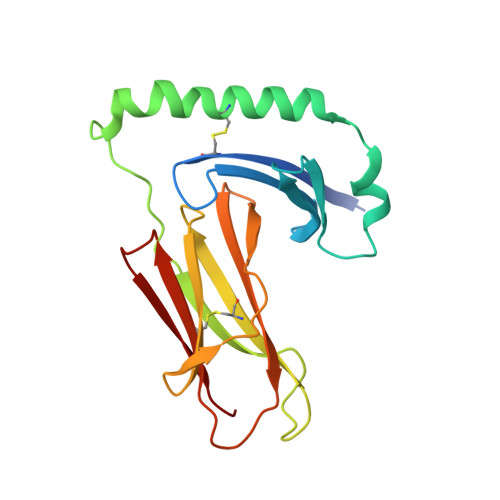
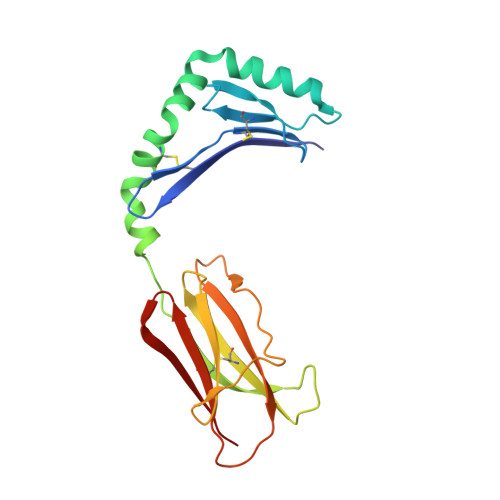
Crystal structure of mouse H2-M.
Fremont, D.H., Crawford, F., Marrack, P., Hendrickson, W.A., Kappler, J.(1998) Immunity 9: 385-393
- PubMed: 9768758
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80621-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1K8I - PubMed Abstract:
H2-M (HLA-DM in humans) resides in an acidic endosomal compartment, where it facilitates the loading of antigenic peptides into the peptide-binding groove of class II MHC. The crystal structure of a soluble form of H2-M has been solved to 3.1 A resolution, revealing a heterodimer with structural similarities to the MHC family of proteins. In contrast to its antigen-presenting cousins, the membrane distal alpha helices of H2-M pack closely together, occluding most of the binding groove except for a single large pocket near the center. The structure of H2-M has several unique features that may play a role in its function as a molecular chaperone and peptide exchange factor.
- Center for Immunology, Department of Pathology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri 63110, USA. fremont@immunology.wustl.edu
Organizational Affiliation: