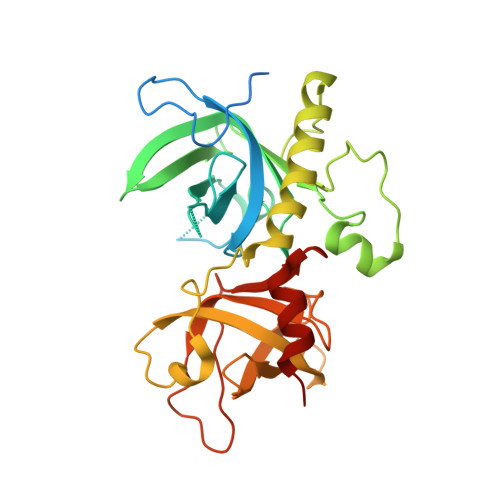
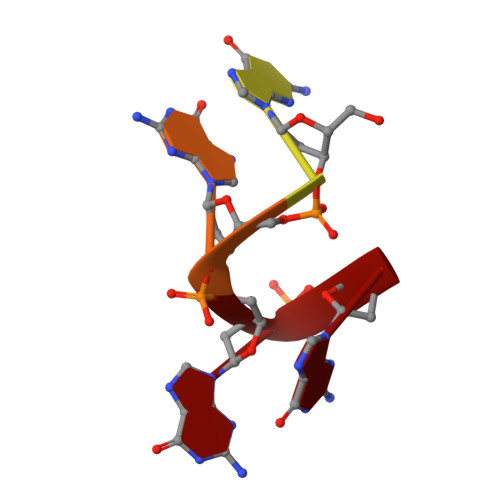
Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of Oxytricha nova telomere end-binding protein alpha subunit both uncomplexed and complexed with telomeric ssDNA.
Classen, S., Ruggles, J.A., Schultz, S.C.(2001) J Mol Biology 314: 1113-1125
- PubMed: 11743727
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.5191
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1K8G - PubMed Abstract:
Oxytricha nova telomere end-binding protein specifically recognizes and caps single strand (T(4)G(4))(n) telomeric DNA at the very 3'-ends of O. nova macronuclear chromosomes. Proteins homologous to the N-terminal domain of OnTEBP alpha subunit have now been identified in Oxytricha trifallax, Stylonychia mytilis, Euplotes crassus, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and Homo sapiens, suggesting that this protein is widely distributed in eukaryotes. We describe here the crystal structures of the N-terminal single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding domain of O. nova telomere end-binding protein alpha subunit both uncomplexed and complexed with single strand telomeric DNA. These structures show how the N-terminal domain of alpha alone, in the absence of the beta subunit and without alpha dimerization, can bind single-stranded telomeric DNA in a sequence-specific and 3'-end-specific manner. Furthermore, comparison of the uncomplexed and complexed forms of this protein shows that the ssDNA-binding site is largely pre-organized in the absence of ssDNA with modest, but interesting, rearrangements of amino acid side-chains that compose the ssDNA-binding site. The structures described here extend our understanding of structures of O. nova telomeric complexes by adding uncomplexed and complexed forms of monomeric alpha to previously described structures for (alpha 56/ssDNA)(2) dimer and alpha 56/beta 28/ssDNA ternary complexes. We believe that each of these four structures represent intermediates in an ordered assembly/disassembly pathway for O. nova telomeric complexes.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-0215, USA. classen@uclink4.berkeley.edu
Organizational Affiliation: