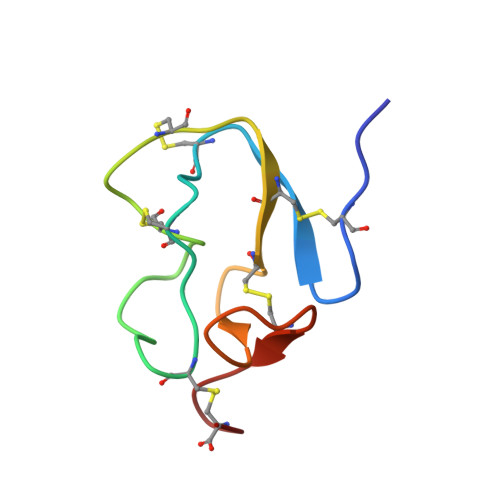
Solution structure of BSTI: a new trypsin inhibitor from skin secretions of Bombina bombina.
Rosengren, K.J., Daly, N.L., Scanlon, M.J., Craik, D.J.(2001) Biochemistry 40: 4601-4609
- PubMed: 11294627
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi002623v
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HX2 - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional solution structure of BSTI, a trypsin inhibitor from the European frog Bombina bombina, has been solved using (1)H NMR spectroscopy. The 60 amino acid protein contains five disulfide bonds, which were unambiguously determined to be Cys (4--38), Cys (13--34), Cys (17--30), Cys (21--60), and Cys (40--54) by experimental restraints and subsequent structure calculations. The main elements of secondary structure are four beta-strands, arranged as two small antiparallel beta-sheets. The overall fold of BSTI is disk shaped and is characterized by the lack of a hydrophobic core. The presumed active site is located on a loop comprising residues 21--34, which is a relatively disordered region similar to that seen in many other protease inhibitors. However, the overall fold is different to other known protease inhibitors with the exception of a small family of inhibitors isolated from nematodes of the family Ascaris and recently also from the haemolymph of Apis mellifera. BSTI may thus be classified as a new member of this recently discovered family of protease inhibitors.
- Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD 4072, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: