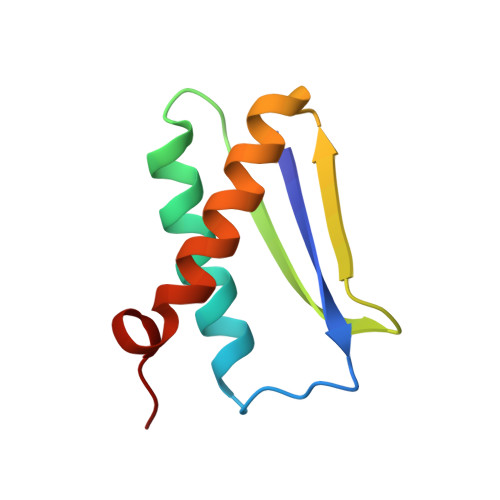
Solution structure of DinI provides insight into its mode of RecA inactivation.
Ramirez, B.E., Voloshin, O.N., Camerini-Otero, R.D., Bax, A.(2000) Protein Sci 9: 2161-2169
- PubMed: 11152126
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.9.11.2161
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GHH - PubMed Abstract:
The Escherichia coli RecA protein triggers both DNA repair and mutagenesis in a process known as the SOS response. The 81-residue E. coli protein DinI inhibits activity of RecA in vivo. The solution structure of DinI has been determined by multidimensional triple resonance NMR spectroscopy, using restraints derived from two sets of residual dipolar couplings, obtained in bicelle and phage media, supplemented with J couplings and a moderate number of NOE restraints. DinI has an alpha/beta fold comprised of a three-stranded beta-sheet and two alpha-helices. The beta-sheet topology is unusual: the central strand is flanked by a parallel and an antiparallel strand and the sheet is remarkably flat. The structure of DinI shows that six negatively charged Glu and Asp residues on DinI's kinked C-terminal alpha-helix form an extended, negatively charged ridge. We propose that this ridge mimics the electrostatic character of the DNA phospodiester backbone, thereby enabling DinI to compete with single-stranded DNA for RecA binding. Biochemical data confirm that DinI is able to displace ssDNA from RecA.
- Laboratory of Chemical Physics, National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20892-0520, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: