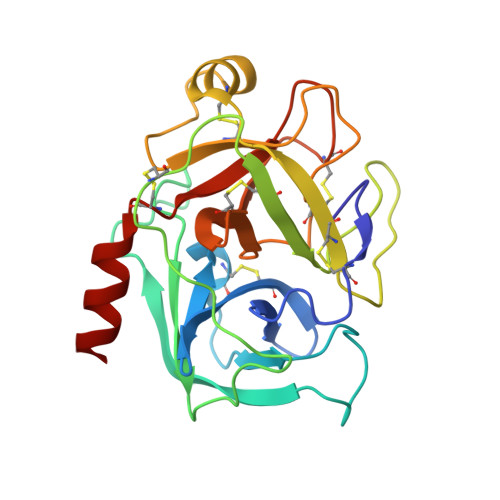
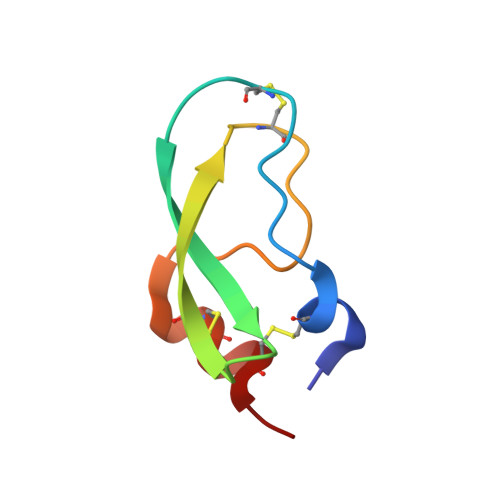
Substitutions at the P(1) position in BPTI strongly affect the association energy with serine proteinases.
Grzesiak, A., Helland, R., Smalas, A.O., Krowarsch, D., Dadlez, M., Otlewski, J.(2000) J Mol Biology 301: 205-217
- PubMed: 10926503
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.3935
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EJM - PubMed Abstract:
The role of the S(1) subsite in trypsin, chymotrypsin and plasmin has been examined by measuring the association with seven different mutants of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI); the mutants contain Gly, Ala, Ser, Val, Leu, Arg, and Trp at the P(1) position of the reactive site. The effects of substitutions at the P(1) position on the association constants are very large, comprising seven orders of magnitude for trypsin and plasmin, and over five orders for chymotrypsin. All mutants showed a decrease of the association constant to the three proteinases in the same order: Ala>Gly>Ser>Arg>Val>Leu>Trp. Calorimetric and circular dichroism methods showed that none of the P1 substitutions, except the P1-Val mutant, lead to destabilisation of the binding loop conformation. The X-ray structure of the complex formed between bovine beta-trypsin and P(1)-Leu BPTI showed that the P(1)-Leu sterically conflicts with the side-chain of P(3)-Ile, which thereby is forced to rotate approximately 90 degrees. Ile18 (P(3)) in its new orientation, in turn interacts with the Tyr39 side-chain of trypsin. Introduction of a large side-chain at the P1' position apparently leads to a cascade of small alterations of the trypsin-BPTI interface that seem to destabilise the complex by it adopting a less optimized packing and by tilting the BPTI molecule up to 15 degrees compared to the native trypsin-BPTI complex.
- Protein Engineering Laboratory, Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Wroclaw, Tamka 2, Wroclaw, 50-137, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: