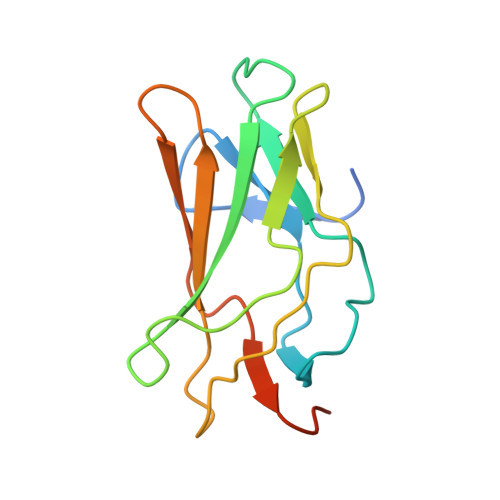
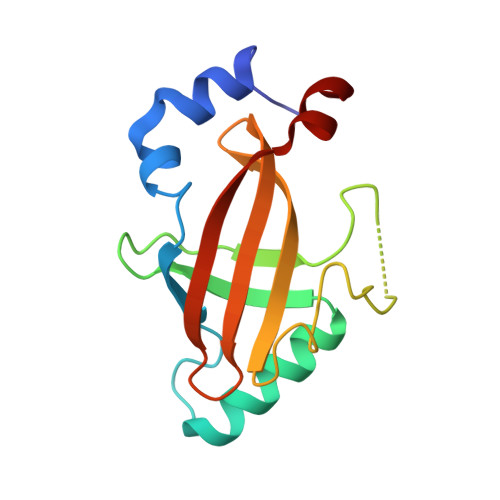
Structural Basis for the Heterodimeric Interaction between the Acute Leukaemia-Associated Transcription Factors Aml1 and Cbfbeta
Warren, A.J., Bravo, J., Williams, R.L., Rabbits, T.H.(2000) EMBO J 19: 3004
- PubMed: 10856244
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.12.3004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1E50 - PubMed Abstract:
Mutations in the genes encoding the interacting proteins AML1 and CBFbeta are the most common genetic abnormalities in acute leukaemia, and congenital mutations in the related AML3 gene are associated with disorders of osteogenesis. Furthermore, the interaction of AML1 with CBFbeta is essential for haematopoiesis. We report the 2.6 A resolution crystal structure of the complex between the AML1 Runt domain and CBFbeta, which represents a paradigm for the mode of interaction of this highly conserved family of transcription factors. The structure demonstrates that point mutations associated with cleidocranial dysplasia map to the conserved heterodimer interface, suggesting a role for CBFbeta in osteogenesis, and reveals a potential protein interaction platform composed of conserved negatively charged residues on the surface of CBFbeta.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QH, UK. ajw@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
Organizational Affiliation: