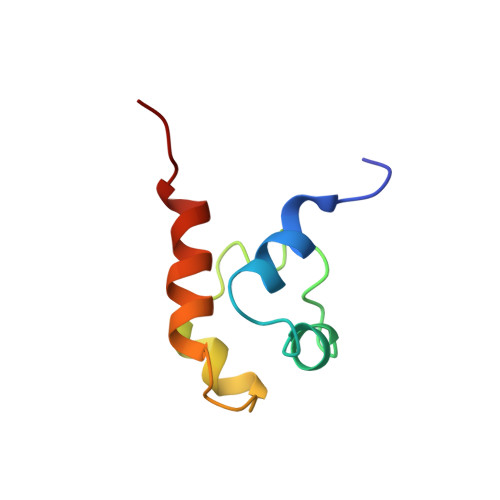
Solution structure of a conserved C-terminal domain of p73 with structural homology to the SAM domain.
Chi, S.W., Ayed, A., Arrowsmith, C.H.(1999) EMBO J 18: 4438-4445
- PubMed: 10449409
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.16.4438
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1COK - PubMed Abstract:
p73 and p63 are two recently cloned genes with homology to the tumor suppressor p53, whose protein product is a key transcriptional regulator of genes involved in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. While all three proteins share conserved transcriptional activation, DNA-binding and oligomerization domains, p73 and p63 have an additional conserved C-terminal region. We have determined the three-dimensional solution structure of this conserved C-terminal domain of human p73. The structure reveals a small five-helix bundle with striking similarity to the SAM (sterile alpha motif) domains of two ephrin receptor tyrosine kinases. The SAM domain is a putative protein-protein interaction domain found in a variety of cytoplasmic signaling proteins and has been shown to form both homo- and hetero-oligomers. However, the SAM-like C-terminal domains of p73 and p63 are monomeric and do not interact with one another, suggesting that this domain may interact with additional, as yet uncharacterized proteins in a signaling and/or regulatory role.
- Ontario Cancer Institute and Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, 610 University Avenue, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5G 2M9.
Organizational Affiliation: