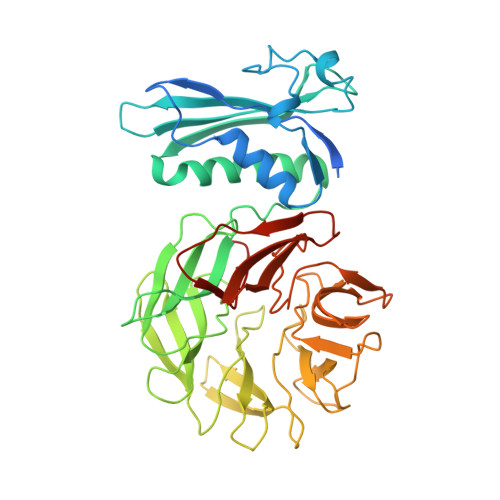
The structure of TolB, an essential component of the tol-dependent translocation system, and its protein-protein interaction with the translocation domain of colicin E9.
Carr, S., Penfold, C.N., Bamford, V., James, R., Hemmings, A.M.(2000) Structure 8: 57-66
- PubMed: 10673426
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00079-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1C5K - PubMed Abstract:
E colicin proteins have three functional domains, each of which is implicated in one of the stages of killing Escherichia coli cells: receptor binding, translocation and cytotoxicity. The central (R) domain is responsible for receptor-binding activity whereas the N-terminal (T) domain mediates translocation, the process by which the C-terminal cytotoxic domain is transported from the receptor to the site of its cytotoxicity. The translocation of enzymatic E colicins like colicin E9 is dependent upon TolB but the details of the process are not known. We have demonstrated a protein-protein interaction between the T domain of colicin E9 and TolB, an essential component of the tol-dependent translocation system in E. coli, using the yeast two-hybrid system. The crystal structure of TolB, a procaryotic tryptophan-aspartate (WD) repeat protein, reveals an N-terminal alpha + beta domain based on a five-stranded mixed beta sheet and a C-terminal six-bladed beta-propeller domain. The results suggest that the TolB-box residues of the T domain of colicin E9 interact with the beta-propeller domain of TolB. The protein-protein interactions of other beta-propeller-containing proteins, the yeast yPrp4 protein and G proteins, are mediated by the loops or outer sheets of the propeller blades. The determination of the three-dimensional structure of the T domain-TolB complex and the isolation of mutations in TolB that abolish the interaction with the T domain will reveal fine details of the protein-protein interaction of TolB and the T domain of E colicins.
- Colicin Research Group, School of Biological Sciences, School of Chemical Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, NR4 7TJ, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: