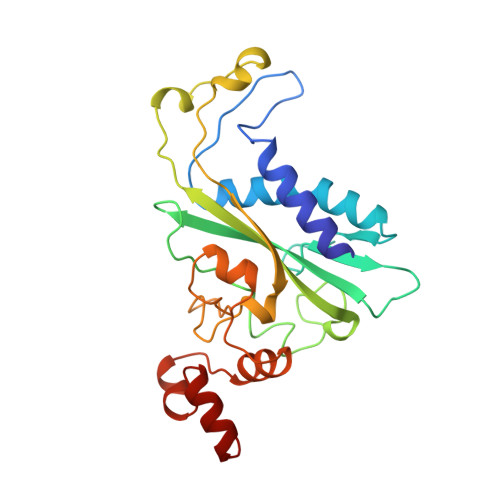
Structural analysis of a mutational hot-spot in the EcoRV restriction endonuclease: a catalytic role for a main chain carbonyl group.
Thomas, M.P., Brady, R.L., Halford, S.E., Sessions, R.B., Baldwin, G.S.(1999) Nucleic Acids Res 27: 3438-3445
- PubMed: 10446231
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/27.17.3438
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1B94, 1B95, 1B96, 1B97 - PubMed Abstract:
Following random mutagenesis of the Eco RV endonuclease, a high proportion of the null mutants carry substitutions at Gln69. Such mutants display reduced rates for the DNA cleavage step in the reaction pathway, yet the crystal structures of wild-type Eco RV fail to explain why Gln69 is crucial for activity. In this study, crystal structures were determined for two mutants of Eco RV, with Leu or Glu at residue 69, bound to specific DNA. The structures of the mutants are similar to the native protein and no function can be ascribed to the side chain of the amino acid at this locus. Instead, the structures of the mutant proteins suggest that the catalytic defect is due to the positioning of the main chain carbonyl group. In the enzyme-substrate complex for Eco RV, the main chain carbonyl of Gln69 makes no interactions with catalytic functions but, in the enzyme-product complex, it coordinates a metal ion bound to the newly liberated 5'-phosphate. This re-positioning may be hindered in the mutant proteins. Molecular dynamics calculations indicate that the metal on the phosphoryl oxygen interacts with the carbonyl group upon forming the pentavalent intermediate during phosphodiester hydrolysis. A main chain carbonyl may thus play a role in catalysis by Eco RV.
- Department of Biochemistry, School of Medical Sciences, University of Bristol, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TD, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: