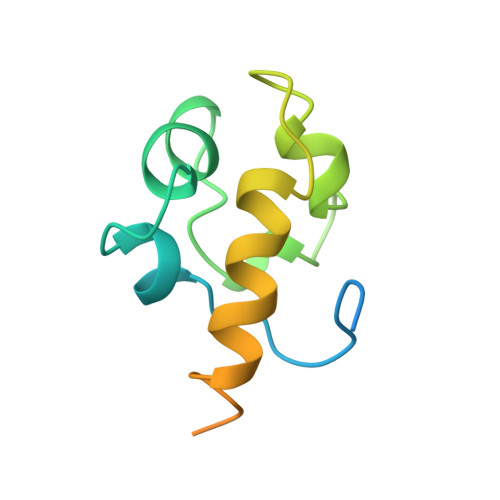
The N-terminal domain of the human Rad51 protein binds DNA: structure and a DNA binding surface as revealed by NMR.
Aihara, H., Ito, Y., Kurumizaka, H., Yokoyama, S., Shibata, T.(1999) J Mol Biology 290: 495-504
- PubMed: 10390347
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1999.2904
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1B22 - PubMed Abstract:
Human Rad51 protein (HsRad51) is a homolog of Escherichia coli RecA protein, and functions in DNA repair and recombination. In higher eukaryotes, Rad51 protein is essential for cell viability. The N-terminal region of HsRad51 is highly conserved among eukaryotic Rad51 proteins but is absent from RecA, suggesting a Rad51-specific function for this region. Here, we have determined the structure of the N-terminal part of HsRad51 by NMR spectroscopy. The N-terminal region forms a compact domain consisting of five short helices, which shares structural similarity with a domain of endonuclease III, a DNA repair enzyme of E. coli. NMR experiments did not support the involvement of the N-terminal domain in HsRad51-HsBrca2 interaction or the self-association of HsRad51 as proposed by previous studies. However, NMR tiration experiments demonstrated a physical interaction of the domain with DNA, and allowed mapping of the DNA binding surface. Mutation analysis showed that the DNA binding surface is essential for double-stranded and single-stranded DNA binding of HsRad51. Our results suggest the presence of a DNA binding site on the outside surface of the HsRad51 filament and provide a possible explanation for the regulation of DNA binding by phosphorylation within the N-terminal domain.
- Cellular & Molecular Biology Laboratory, The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (RIKEN), 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama, 351-0198, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: