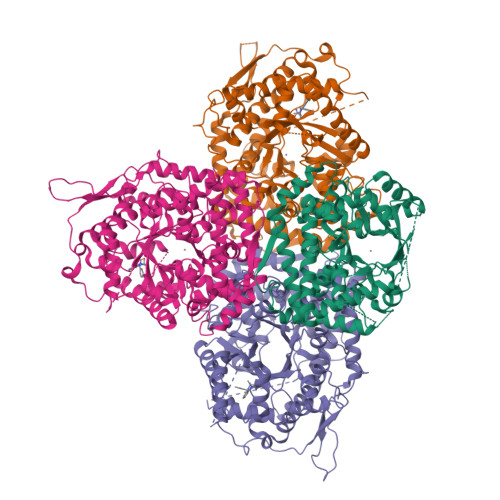
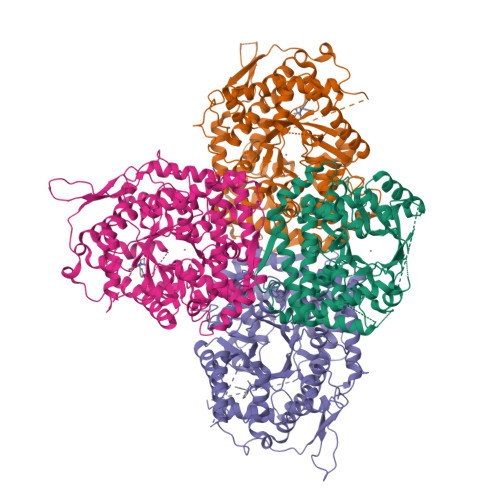
The discovery of 3,3-dimethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline-1-carboxamides as AMPD2 inhibitors with a novel mechanism of action.
Kitao, Y., Saito, T., Watanabe, S., Ohe, Y., Takahashi, K., Akaki, T., Adachi, T., Doi, S., Yamanaka, K., Murai, Y., Oba, M., Suzuki, T.(2023) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 80: 129110-129110
- PubMed: 36563792
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.129110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HU6, 8HUB - PubMed Abstract:
AMP deaminase 2 (AMPD2) has been thought to play an important role in energy homeostasis and immuno-oncology, while selective AMPD2 inhibitors are highly demanded to clarify the physiological function of AMPD2. In this report, we describe selective AMPD2 inhibitors inducing allosteric modulation. Based on hypothesis that compounds that exhibit increased inhibition by preincubation would cause conformational change of the enzyme, starting from HTS hit compound 4, we discovered compound 8 through the SAR study. From X-ray structural information of 8, this chemical series has a novel mechanism of action that changes the substrate pocket to prevent AMP from binding. Further elaboration of compound 8 led to the tool compound 21 which exhibited potent inhibitory activity of AMPD2 in ex vivo evaluation of mouse liver.
Organizational Affiliation:
Chemical Research Laboratories, Central Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Japan Tobacco Inc, 1-1, Murasaki-cho, Takatsuki, Osaka 569-1125, Japan; Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 1-5 Shimogamohangi-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-0823, Japan. Electronic address: yuki.kitao@jt.com.